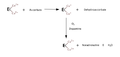Dopamine beta-hydroxylase: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Dopamine_beta-monooxygenase_reaction.svg|Dopamine beta-monooxygenase reaction | |||
File:DBH_mechanism.png|DBH mechanism | |||
File:Models_for_Oligomer_Structures_of_DBH.png|Models for Oligomer Structures of DBH | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:04, 18 February 2025
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), also known as dopamine beta-monooxygenase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine.
Function[edit]
DBH is a copper-containing oxygenase that exists as a tetramer with four identical subunits. It is located in the synaptic vesicles of postganglionic sympathetic neurons and in adrenal medulla, where it converts dopamine to norepinephrine. This conversion is a critical step in the sympathetic nervous system's production of norepinephrine, which plays a key role in the body's fight or flight response.
Clinical significance[edit]
Mutations in the DBH gene can lead to Dopamine beta hydroxylase deficiency, a condition characterized by a lack of norepinephrine and epinephrine in patients. Symptoms can include orthostatic hypotension, ptosis, and nasal stuffiness.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />