Calcar avis: Difference between revisions
Tag: Manual revert |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category:Brain]] | [[Category:Brain]] | ||
{{anatomy-stub}} | {{anatomy-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray739-emphasizing-calcar-avis.png|Gray's Anatomy illustration emphasizing the calcar avis | |||
File:Gray738.png|Gray's Anatomy illustration of the brain | |||
File:Human_brain_right_dissected_lateral_view_description.JPG|Human brain right dissected lateral view | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:02, 18 February 2025
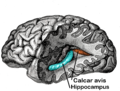
Calcar avis is a small bony structure found in the human brain. It is also known as the bird's spur. The calcar avis is located in the medial part of the occipital lobe, specifically in the cerebral hemispheres. It is visible in the coronal plane of the brain, and is formed by the backward and inward folding of the occipital lobe.
Anatomy[edit]
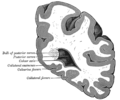
The calcar avis is a prominent bulge that is visible in the posterior horn of the lateral ventricle. It is caused by the calcarine sulcus, a deep fissure in the occipital lobe. The calcar avis is located above the hippocampus and below the splenium of the corpus callosum.
Function[edit]
The calcar avis is associated with the processing of visual information. It is located near the primary visual cortex, which is responsible for processing visual stimuli. The calcar avis is thought to play a role in the perception of visual stimuli, although its exact function is not fully understood.
Clinical significance[edit]
The absence or deformation of the calcar avis can be an indicator of certain neurological conditions. For example, it is often absent in cases of schizencephaly, a rare developmental disorder characterized by abnormal slits or clefts in the cerebral hemispheres. The presence and shape of the calcar avis can also be used to identify and differentiate between certain types of brain malformations.
See also[edit]
-
Gray's Anatomy illustration emphasizing the calcar avis
-
Gray's Anatomy illustration of the brain
-
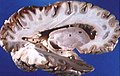
Human brain right dissected lateral view