Intracranial dolichoectasias: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
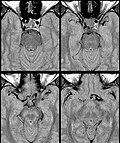
File:Dolichoectasia_of_the_left_internal_carotid_artery_patientcase_image2.jpg|Dolichoectasia of the left internal carotid artery | |||
File:Dolichoectasia_of_the_left_internal_carotid_artery_patientcase_image1.jpg|Dolichoectasia of the left internal carotid artery | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 02:13, 18 February 2025
Intracranial Dolichoectasias is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement and elongation of arteries in the brain. This condition is often associated with cerebrovascular disease and can lead to serious complications such as stroke and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Intracranial Dolichoectasias can vary greatly depending on the severity and location of the affected arteries. Common symptoms may include:
Causes
The exact cause of Intracranial Dolichoectasias is unknown. However, it is believed to be associated with certain risk factors such as:
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Intracranial Dolichoectasias is typically made through imaging studies such as MRI or CT scan. These tests can help to visualize the arteries in the brain and identify any abnormalities.
Treatment
Treatment for Intracranial Dolichoectasias is primarily focused on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
- Medication to control blood pressure and reduce the risk of stroke
- Surgery to repair or bypass affected arteries in severe cases
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with Intracranial Dolichoectasias can vary greatly depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. However, with appropriate treatment and management, many individuals can lead a normal life.