Lipoamide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Coenzymes]] | [[Category:Coenzymes]] | ||
[[Category:Enzymes]] | [[Category:Enzymes]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
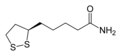
File:Lipoamide-2D-skeletal.png|2D Skeletal Structure of Lipoamide | |||
File:Lipoamide-3D-vdW.png|3D Van der Waals Model of Lipoamide | |||
File:PyruvateDehyRxn.png|Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Reaction | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 18 February 2025
Lipoamide is a coenzyme that plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes within the human body. It is an essential component of several enzyme complexes, including pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which are involved in energy production through the citric acid cycle.
Structure and Function[edit]
Lipoamide, also known as lipoic acid or thioctic acid, is a sulfur-containing compound with a unique structure. It consists of a five-membered ring with two sulfur atoms at adjacent positions. This structure allows lipoamide to act as a versatile cofactor in enzymatic reactions.
Lipoamide functions as a carrier of acyl groups during metabolic reactions. It undergoes reversible oxidation and reduction reactions, shuttling acetyl groups between different enzymes. This process is crucial for the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, which is a key step in the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Role in Energy Production[edit]
One of the primary functions of lipoamide is its involvement in energy production. It acts as a cofactor for the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which converts pyruvate, a product of glycolysis, into acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where it is further oxidized to generate ATP, the main energy currency of the cell.
Lipoamide also plays a vital role in the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which is involved in the metabolism of amino acids. This complex converts alpha-ketoglutarate, a product of amino acid breakdown, into succinyl-CoA, another intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Lipoamide deficiency can lead to various metabolic disorders. For example, defects in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which relies on lipoamide as a cofactor, can result in a condition called pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. This disorder impairs the body's ability to convert pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, leading to a buildup of pyruvate and lactic acid in the blood, causing neurological symptoms.
Lipoamide has also gained attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. It exhibits antioxidant properties and has been studied for its role in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Additionally, lipoamide supplementation has shown promise in the management of certain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy.
References[edit]
<references>
See Also[edit]
-
2D Skeletal Structure of Lipoamide
-
3D Van der Waals Model of Lipoamide
-
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Reaction