Nissen fundoplication: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
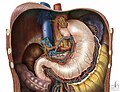
File:Nissen_fundoplication.png|Nissen fundoplication | |||
File:Watercolour_of_the_Nissen-method.jpg|Watercolour of the Nissen method | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Nissen_fundoplication.png|Nissen fundoplication | File:Nissen_fundoplication.png|Nissen fundoplication | ||
File:Watercolour_of_the_Nissen-method.jpg|Watercolour of the Nissen method | File:Watercolour_of_the_Nissen-method.jpg|Watercolour of the Nissen method | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 02:01, 18 February 2025
Nissen fundoplication is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia. In this procedure, the upper part of the stomach (fundus) is wrapped around the lower end of the esophagus and stitched into place. This strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter, preventing acid reflux and repairing a hiatal hernia.
Procedure
The Nissen fundoplication procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope and other surgical instruments. The upper part of the stomach is then wrapped around the lower end of the esophagus and stitched into place. This creates a new barrier between the stomach and esophagus, which prevents the backflow of stomach acid.
Indications
Nissen fundoplication is indicated for patients with severe GERD symptoms that are not controlled by medication. It is also used to treat hiatal hernias.
Risks and Complications
Like all surgeries, Nissen fundoplication carries risks, including infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Specific complications related to this procedure include difficulty swallowing, bloating, and flatulence. In rare cases, the wrap may become too tight and cause difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Postoperative Care
After the procedure, patients are usually able to return home the same day or the next day. They are advised to eat soft foods for a few weeks and gradually return to their normal diet. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor recovery and assess the effectiveness of the procedure.