Chromate and dichromate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
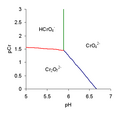
File:Predominance_diagram_Cr.png|Chromate and dichromate predominance diagram | |||
File:Laidlaw_school_bus.jpg|Chromate and dichromate | |||
File:Crocoite_from_Tasmania.jpg|Crocoite from Tasmania | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:00, 18 February 2025
Chromate and Dichromate are chemical compounds containing the chromate (CrO4^2-) and dichromate (Cr2O7^2-) ions, respectively. These compounds are oxoanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state, also known as hexavalent chromium. Chromates and dichromates are highly corrosive and are used in a variety of industrial processes, including as pigments in paints, inks, and plastics, and in the tanning of leather. They are also important in the manufacture of chromic acid and in electroplating.
Chemistry[edit]
Chromate and dichromate ions are interconvertible in aqueous solution, depending on the pH. At high pH, the chromate ion (CrO4^2-) predominates, while at low pH, the dichromate ion (Cr2O7^2-) is more stable. This equilibrium can be represented by the following chemical equation:
CrO4^2- + 2H+ ↔ Cr2O7^2- + H2O
Chromates and dichromates are strong oxidizing agents and can react with a variety of organic and inorganic substances. They are also known to be carcinogenic and pose significant environmental and health risks if not handled properly.
Uses[edit]
Chromate and dichromate compounds have a wide range of applications. They are used in the production of chromium-based pigments, which are used to impart yellow, orange, and red colors to paints, inks, and plastics. These compounds are also used in the tanning of leather, as oxidizing agents in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of chromic acid, which is used in chrome plating and as a corrosion inhibitor.
Health and Environmental Concerns[edit]
Hexavalent chromium compounds, including chromates and dichromates, are highly toxic and carcinogenic. Exposure to these compounds can lead to severe respiratory problems, skin ulcers, and lung cancer. Due to their high toxicity, the use and disposal of chromate and dichromate compounds are strictly regulated in many countries.
Environmental exposure to chromates and dichromates can occur through the improper disposal of industrial waste, leading to contamination of water and soil. These compounds are highly soluble in water, making them a significant environmental pollutant that can affect aquatic life and enter the food chain.
Regulation and Safety[edit]
Due to the health and environmental risks associated with chromate and dichromate compounds, their use is regulated by various international and national agencies. Workers handling these compounds are required to use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and industries using these chemicals must adhere to strict waste management and disposal protocols to minimize environmental contamination.
Conclusion[edit]
Chromate and dichromate compounds play a significant role in various industrial applications but pose serious health and environmental risks. Proper handling, use, and disposal of these compounds are essential to minimize their adverse effects.
-
Chromate and dichromate predominance diagram
-
Chromate and dichromate
-
Crocoite from Tasmania