Glaucine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Glaucine.svg|Glaucine | |||
File:(S)-Glaucin_V2.svg|(S)-Glaucine | |||
File:(R)-Glaucin_V2.svg|(R)-Glaucine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:57, 18 February 2025
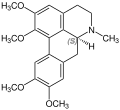
Glaucine is an alkaloid found in several different plant species in the Papaveraceae family such as Glaucium flavum (yellow hornpoppy) and Corydalis yanhusuo, and Dicentra cucullaria. It has bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory effects, acting as a PDE4 inhibitor and calcium channel blocker, and is used medically as an antitussive in some countries. Glaucine may produce side effects such as sedation, fatigue, and a hallucinogenic effect characterised by colourful visual images, and is used recreationally for its psychedelic properties.
Chemistry[edit]
Glaucine is in the benzylisoquinoline class of alkaloids. It is extracted from its natural plant sources using ethanol, and can then be further synthesized into its derivative forms for various uses.
Pharmacology[edit]
Glaucine has a dual mechanism of action, acting as a PDE4 inhibitor and a calcium channel blocker, which leads to its bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory effects. It is used medically as an antitussive, or cough suppressant, in some countries.
Side Effects[edit]
Possible side effects of glaucine include sedation, fatigue, and a hallucinogenic effect characterised by colourful visual images. These psychedelic properties have led to the recreational use of glaucine.
Recreational Use[edit]
Due to its hallucinogenic effects, glaucine is used recreationally for its psychedelic properties. However, it is not widely known or used for this purpose, and is not classified as a controlled substance in most countries.