Modelling biological systems: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[Category:Mathematical and Theoretical Biology]] | [[Category:Mathematical and Theoretical Biology]] | ||
{{biology-stub}} | {{biology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
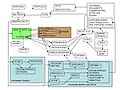
File:Signal_transduction_pathways.svg|Signal transduction pathways | |||
File:EltonFW.jpg|Elton's food web | |||
File:Lotka_Volterra_dynamics.svg|Lotka-Volterra dynamics | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:36, 18 February 2025
Modelling Biological Systems is a complex and interdisciplinary field that focuses on the development of theoretical, mathematical, and computational models to study biological, ecological, and biomedical systems. The primary goal of modelling biological systems is to enhance our understanding of life's processes, from the molecular level to the ecosystem level, and to apply this knowledge in fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and conservation biology.
Overview[edit]
Biological systems are inherently complex, consisting of numerous interacting components that give rise to the dynamic behavior observed in living organisms. Modelling these systems requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining principles from biology, physics, chemistry, mathematics, and computer science. Models can range from simple, abstract representations to highly detailed simulations that mimic biological processes.
Types of Models[edit]
There are several types of models used in the study of biological systems, including:
- Mathematical Models - These models use mathematical equations to describe the behavior of a system. They are particularly useful for understanding the dynamics of population growth, the spread of diseases, and enzyme kinetics.
- Computational Models - These models employ algorithms and computer simulations to study complex systems that are difficult to mathematically analyze. Computational models are widely used in genomics, protein folding, and systems biology.
- Statistical Models - These models apply statistical methods to analyze and interpret biological data. They are essential in epidemiology, genetics, and ecology for making predictions and understanding variability and uncertainty in biological systems.
Applications[edit]
Modelling biological systems has a wide range of applications in science and engineering, including:
- Drug Discovery and Development - Models can predict how drugs interact with biological systems, helping to identify potential drug targets and optimize drug efficacy and safety.
- Disease Modelling - By simulating the spread of diseases and the immune system's response, models can inform public health strategies and vaccine development.
- Ecosystem Management - Models of ecosystems can assist in conservation efforts, predicting the impact of environmental changes and human activities on biodiversity.
- Synthetic Biology - Computational models guide the design of synthetic biological systems with desired properties, advancing the development of biofuels, bioplastics, and pharmaceuticals.
Challenges[edit]
Despite their potential, modelling biological systems faces several challenges, including the complexity of biological systems, the need for accurate and comprehensive data, and the limitations of current modelling techniques. Ongoing research aims to address these challenges by developing more sophisticated models, improving data collection methods, and integrating different types of models for a more comprehensive understanding of biological systems.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>

-
Signal transduction pathways
-
Elton's food web
-
Lotka-Volterra dynamics