Nasopalatine nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
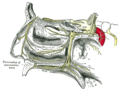
File:Gray858.png|Nasopalatine nerve | |||
File:Gray780.png|Nasopalatine nerve | |||
File:Gray187.png|Nasopalatine nerve | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:22, 18 February 2025
Nasopalatine nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve that plays a crucial role in the sensory innervation of the nasal cavity and the hard palate. It is also known as the anterior palatine nerve or incisive nerve.
Etymology[edit]
The term "nasopalatine" is derived from the Latin words "nasus" meaning nose and "palatum" meaning roof of the mouth. The nerve is so named because it supplies the nasal cavity and the hard palate.
Anatomy[edit]
The nasopalatine nerve originates from the Pterygopalatine ganglion, a parasympathetic ganglion located in the pterygopalatine fossa. It travels through the sphenopalatine foramen into the nasal cavity, where it gives off several branches to supply the nasal septum and the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. It then continues forward to the incisive canal, through which it reaches the hard palate.
Function[edit]
The nasopalatine nerve carries sensory information from the nasal cavity and the hard palate to the brain. This includes sensations of touch, temperature, and pain. It also plays a role in the perception of taste from the anterior part of the hard palate.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the nasopalatine nerve can result in loss of sensation in the nasal cavity and the hard palate. This can occur as a result of trauma, surgery, or certain medical conditions. In some cases, it may also lead to altered taste perception.
Related terms[edit]
- Maxillary nerve: The parent nerve of the nasopalatine nerve.
- Pterygopalatine ganglion: The origin of the nasopalatine nerve.
- Sphenopalatine foramen: The passage through which the nasopalatine nerve enters the nasal cavity.
- Incisive canal: The canal through which the nasopalatine nerve reaches the hard palate.