WIN 55,212-2: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:WIN_55,212-2-2D-skeletal.svg|WIN 55,212-2 2D Skeletal Structure | |||
File:Pancreatic_stellate_cell_cropped.png|Pancreatic Stellate Cell | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:18, 18 February 2025
WIN 55,212-2 is a chemical compound that is often used in scientific research. It is a synthetic cannabinoid and a potent agonist that binds to cannabinoid receptors in the body. WIN 55,212-2 is known for its ability to mimic the effects of naturally occurring cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active compound in cannabis.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
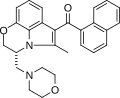
WIN 55,212-2 is a derivative of naphthalen-1-yl-(1-pentylindol-3-yl)methanone. It has a molecular formula of C27H26O3 and a molecular weight of 426.49 g/mol. The compound is usually presented as a racemic mixture, with the (R)-enantiomer being the active form.
Pharmacology[edit]
WIN 55,212-2 acts as a full agonist at the CB1 receptor and has a high affinity for the CB2 receptor. The compound's effects are similar to those of other cannabinoids, such as analgesia, anti-inflammatory effects, and appetite stimulation. However, it also has some unique properties, such as neuroprotective effects, which have been studied in the context of conditions like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Research and Clinical Use[edit]
While WIN 55,212-2 is not used clinically, it is widely used in research due to its potent and selective activity at the cannabinoid receptors. Studies have investigated its potential therapeutic effects in a range of conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, pain, inflammation, and cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential therapeutic applications of this compound.
Safety and Side Effects[edit]
As with other cannabinoids, the use of WIN 55,212-2 can lead to a range of side effects, including dizziness, nausea, and changes in mood. However, these effects are generally mild and transient. The safety profile of WIN 55,212-2 in humans has not been fully established, as most of the research on this compound has been conducted in animal models.
See Also[edit]
-
WIN 55,212-2 2D Skeletal Structure
-
Pancreatic Stellate Cell