Involuntary unemployment: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
{{Economics-stub}} | {{Economics-stub}} | ||
{{Social-issues-stub}} | {{Social-issues-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
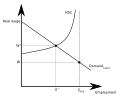
File:Efficiency_wage_Shapiro_Stiglitz.svg|Efficiency wage model by Shapiro and Stiglitz | |||
File:Malinvaud_unemployment_typology.svg|Malinvaud unemployment typology | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:14, 18 February 2025
Involuntary unemployment refers to the state where individuals are willing and able to work at the prevailing wage rate, but cannot find employment. This is different from voluntary unemployment, where individuals choose not to work at the current wage rate. Involuntary unemployment can occur for a variety of reasons, including economic downturns, changes in technology, or structural changes in the economy.
Causes of Involuntary Unemployment[edit]
Involuntary unemployment can be caused by several factors:
- Economic downturns: During periods of economic recession or depression, demand for goods and services decreases, leading to a decrease in demand for labor. This can result in layoffs and increased unemployment.
- Technological changes: Advances in technology can make certain jobs obsolete, leading to structural unemployment. Workers who lack the skills to perform new jobs may find themselves involuntarily unemployed.
- Structural changes: Changes in the structure of the economy, such as the shift from manufacturing to service industries, can also lead to involuntary unemployment. Workers in declining industries may struggle to find new jobs in growing industries.
Effects of Involuntary Unemployment[edit]
Involuntary unemployment can have several negative effects:
- Economic effects: High levels of involuntary unemployment can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, which can further exacerbate economic downturns.
- Social effects: Involuntary unemployment can lead to social problems such as increased crime rates, mental health issues, and decreased social cohesion.
- Individual effects: On an individual level, involuntary unemployment can lead to financial hardship, decreased self-esteem, and mental health issues.
Policies to Address Involuntary Unemployment[edit]
Various policies can be implemented to address involuntary unemployment:
- Education and training: Providing education and training can help workers acquire the skills needed for new jobs.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and tax policies can be used to stimulate demand and create jobs.
- Monetary policy: Central banks can use monetary policy to stimulate economic activity and reduce unemployment.
See Also[edit]
- Unemployment
- Voluntary unemployment
- Structural unemployment
- Cyclical unemployment
- Frictional unemployment
This social-issues related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Efficiency wage model by Shapiro and Stiglitz
-
Malinvaud unemployment typology