Uracil: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category:Nucleobases]] | [[Category:Nucleobases]] | ||
[[Category:Pyrimidines]] | [[Category:Pyrimidines]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Uracil.svg|Uracil structure | |||
File:Uracil_tautomers.png|Uracil tautomers | |||
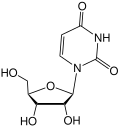
File:Uridin.svg|Uridin structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:12, 18 February 2025
A nucleobase found in RNA
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA, represented by the letter U. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). Uracil is a pyrimidine derivative and is structurally similar to thymine, another pyrimidine found in DNA.
Structure and properties[edit]

Uracil has the chemical formula C4H4N2O2. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that contains a pyrimidine ring. Uracil can exist in several tautomeric forms, which are in equilibrium with each other. The most common tautomer is the keto form.

Role in RNA[edit]
In RNA, uracil base-pairs with adenine through two hydrogen bonds, forming a stable base pair. This pairing is crucial for the structure and function of RNA molecules, including messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Biosynthesis and metabolism[edit]
Uracil is synthesized in the body through the de novo synthesis pathway of pyrimidines. It is also a product of the breakdown of cytosine. In the cell, uracil is converted into uridine by the addition of a ribose sugar, which is then phosphorylated to form uridine monophosphate (UMP).

Applications and significance[edit]
Uracil and its derivatives have several applications in biochemistry and medicine. They are used in the synthesis of various drugs and are important in the study of genetic code and protein synthesis.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
- Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, John L.; Stryer, Lubert (2002). Biochemistry. 5th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4684-0.
- Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G. (2011). Biochemistry. 4th ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-57095-1.
-
Uracil structure
-
Uracil tautomers
-
Uridin structure