Daunosamine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Daunorubicin2DACS.svg|Daunorubicin 2D Structure | |||
File:Idarubicin.svg|Idarubicin Structure | |||
File:Doxorubicin_Structure.png|Doxorubicin Structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:12, 18 February 2025
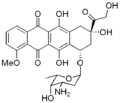
Daunosamine[edit]
Daunosamine is a crucial component of the potent anticancer drug daunorubicin. It is a type of aminosugar that plays a key role in the mechanism of action of daunorubicin, which is commonly used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including leukemia and solid tumors.
Structure and Function[edit]
Daunosamine is a deoxysugar that is attached to the anthracycline core structure of daunorubicin. This aminosugar moiety is essential for the biological activity of the drug. Daunosamine is responsible for the specific interactions of daunorubicin with its molecular targets in cancer cells, leading to inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis, ultimately resulting in cell death.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Daunorubicin, with daunosamine as a critical component, exerts its anticancer effects by intercalating into the DNA of cancer cells, disrupting the DNA replication process, and inducing DNA damage. Additionally, daunorubicin generates reactive oxygen species that further contribute to its cytotoxic effects on cancer cells.
Clinical Applications[edit]
Daunorubicin, containing daunosamine, is used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and certain types of solid tumors. It is often administered in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents as part of a multidrug regimen.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects associated with daunorubicin therapy include myelosuppression, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and increased susceptibility to infections. Cardiotoxicity is a significant concern with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, including daunorubicin, and requires close monitoring during treatment.
-
Daunorubicin 2D Structure
-
Idarubicin Structure
-
Doxorubicin Structure