Pulmonary laceration: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
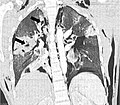
File:Lung_lacerations.JPG|Lung lacerations | |||
File:Pneumothorax_CT.jpg|Pneumothorax CT scan | |||
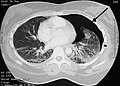
File:Pulmonary_contusion.jpg|Pulmonary contusion | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:10, 18 February 2025
Pulmonary laceration is a medical condition that involves a tear or puncture in the lung tissue. This can occur as a result of blunt or penetrating trauma, such as a car accident or a stab wound. The laceration can lead to a buildup of air or blood in the pleural space, which can cause the lung to collapse.
Causes
Pulmonary lacerations are most commonly caused by trauma to the chest. This can occur in a variety of ways, including:
- Car accidents
- Falls from a height
- Stab wounds
- Gunshot wounds
- Surgical procedures on the chest or lungs
Symptoms
The symptoms of a pulmonary laceration can vary depending on the severity of the injury. They may include:
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Coughing up blood
- Rapid heart rate
- Low blood pressure
Diagnosis
A pulmonary laceration is typically diagnosed through a combination of a physical examination and imaging tests. These may include:
Treatment
The treatment for a pulmonary laceration depends on the severity of the injury. In some cases, the laceration may heal on its own with rest and observation. In more severe cases, surgery may be required to repair the laceration and remove any blood or air that has built up in the pleural space.