PCSK9: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:PDB_2p4e_EBI.png|PCSK9 structure | |||
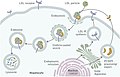
File:PCSK9-mediated_degradation_of_LDLR.jpg|PCSK9-mediated degradation of LDLR | |||
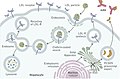
File:PCSK9_inhibition.jpg|PCSK9 inhibition | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:09, 18 February 2025
PCSK9 (Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PCSK9 gene. It is involved in the regulation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, acting as a chaperone for LDL receptors in the liver. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a rare form of familial hypercholesterolemia.
Function[edit]
PCSK9 is an enzyme which functions to degrade low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLR) on hepatocytes; a process that results in higher concentrations of LDL in the bloodstream. The LDLR is responsible for the uptake of circulating LDL into the liver where it is broken down. By promoting the degradation of LDLR, PCSK9 indirectly increases the amount of LDL cholesterol in the blood.
Clinical significance[edit]
Mutations in the PCSK9 gene can lead to either hypocholesterolemia or hypercholesterolemia. Gain-of-function mutations, which increase the activity of PCSK9, result in familial hypercholesterolemia. These mutations increase the degradation of LDLR and therefore decrease the uptake of LDL cholesterol into the liver. This results in high levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood, which can lead to atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Loss-of-function mutations, which decrease the activity of PCSK9, result in hypocholesterolemia. These mutations decrease the degradation of LDLR and therefore increase the uptake of LDL cholesterol into the liver. This results in low levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood.
Therapeutic use[edit]
Inhibitors of PCSK9 are used as a treatment for hypercholesterolemia. These drugs work by binding to PCSK9 and preventing it from degrading LDLR. This increases the uptake of LDL cholesterol into the liver and decreases the amount of LDL cholesterol in the blood.
See also[edit]
- Low-density lipoprotein receptor
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hypocholesterolemia
- Atherosclerosis
- Coronary heart disease
References[edit]
<references />