Aspartic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Glucogenic amino acids]] | [[Category:Glucogenic amino acids]] | ||
{{amino acid-stub}} | {{amino acid-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:L-Asparaginsäure_-_L-Aspartic_acid.svg|L-Aspartic acid structure | |||
File:Aspartic_acid-spin.gif|Aspartic acid 3D model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:59, 18 February 2025
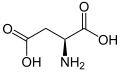
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D) is an amino acid that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is classified as a non-essential amino acid, meaning that it can be synthesized by the human body. Aspartic acid is also a component of many foods and dietary supplements.
Chemical structure[edit]
Aspartic acid has a carboxylate anion side chain, which gives it a negative charge at physiological pH. This property makes it a polar, negatively charged, acidic amino acid. The chemical formula of aspartic acid is C4H7NO4.
Biological role[edit]
Aspartic acid plays a vital role in the citric acid cycle, or Krebs cycle, which is the process that generates energy through the oxidation of acetate into carbon dioxide. In the cycle, aspartic acid contributes to the production of oxaloacetate, which is a key intermediate in the cycle.
Aspartic acid is also involved in the synthesis of other amino acids, as well as in the synthesis of certain nucleotides. It is a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate, and it plays a role in the functioning of the nervous system.
Dietary sources[edit]
Aspartic acid is found in a variety of foods, including animal sources such as poultry, beef, and fish, and plant sources such as legumes, nuts, and grains. It is also a component of aspartame, an artificial sweetener.
Health effects[edit]
While aspartic acid is generally considered safe, excessive consumption can lead to an overabundance of the neurotransmitter glutamate, which can cause excitotoxicity and damage to nerve cells. However, this is usually only a concern with very high intake levels.
See also[edit]
This amino acid related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
L-Aspartic acid structure
-
Aspartic acid 3D model