Acremonium strictum: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:Opportunistic pathogens]] | [[Category:Opportunistic pathogens]] | ||
[[Category:Hypocreales]] | [[Category:Hypocreales]] | ||
== Acremonium strictum == | |||
<gallery> | |||
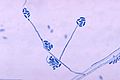
File:Conidia_and_conidiophores_of_the_fungus_Acremonium_falciforme_PHIL_4168_lores.jpg|Conidia and conidiophores of the fungus Acremonium falciforme | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 17 February 2025
Acremonium strictum

Acremonium strictum is a species of fungus in the genus Acremonium. It is known for its role as both a saprophyte and an opportunistic pathogen. This fungus is commonly found in soil and decaying plant material, and it can also be isolated from indoor environments.
Morphology[edit]
Acremonium strictum is characterized by its slow-growing, compact colonies that are initially white and become pinkish or grayish with age. The conidia are typically one-celled, hyaline, and are produced in slimy heads at the tips of simple or branched conidiophores.
Habitat[edit]
This fungus is widely distributed in nature and can be found in various environments, including soil, plant debris, and indoor settings. It thrives in moist conditions and is often isolated from water-damaged buildings.
Pathogenicity[edit]
While Acremonium strictum is primarily a saprophytic organism, it can act as an opportunistic pathogen in humans, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Infections can manifest as mycetoma, onychomycosis, or keratitis.
Clinical Significance[edit]
In clinical settings, Acremonium strictum is recognized for its potential to cause infections in humans. It is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of this organism, especially in patients with weakened immune systems. Diagnosis typically involves culture and microscopic examination of clinical specimens.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of infections caused by Acremonium strictum can be challenging due to its resistance to certain antifungal agents. Management often involves the use of antifungal medications such as voriconazole or posaconazole, along with surgical intervention in some cases.
Related pages[edit]
Acremonium strictum[edit]
-
Conidia and conidiophores of the fungus Acremonium falciforme