Sphenoidal lingula: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
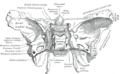
File:Gray145.png|Sphenoidal lingula - Image 1 | |||
File:Gray193.png|Sphenoidal lingula - Image 2 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:07, 17 February 2025
Sphenoidal Lingula is a small, bony structure found in the human skull. It is part of the sphenoid bone, which is located at the base of the skull and connects with all other cranial bones. The sphenoidal lingula is named for its tongue-like shape, with "lingula" being derived from the Latin word for "little tongue".
Etymology[edit]
The term "sphenoidal lingula" comes from the Latin word "sphenoides", meaning "wedge-shaped", and "lingula", meaning "little tongue". This is due to the structure's wedge-like shape and its tongue-like protrusion.
Anatomy[edit]
The sphenoidal lingula is a small, bony protrusion that extends from the medial part of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It is located near the foramen spinosum, a small hole in the skull through which the middle meningeal artery, vein, and nerve pass.
Function[edit]
The sphenoidal lingula serves as a point of attachment for the pterygoid hamulus, a hook-like structure that is part of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. The pterygoid hamulus plays a crucial role in the functioning of the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and equalizes air pressure on either side of the eardrum.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Due to its location and structure, the sphenoidal lingula can be involved in various medical conditions. For instance, it can be damaged during surgical procedures involving the sphenoid bone or the surrounding structures. Moreover, abnormalities or variations in the shape or size of the sphenoidal lingula can potentially lead to complications such as Eustachian tube dysfunction.