Dextrorphan: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
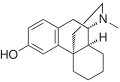
File:Dextrorphan.svg|Dextrorphan | |||
File:Dextrorphane_3d.gif|Dextrorphane 3D | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:05, 17 February 2025
Dextrorphan is a psychoactive drug of the morphinan chemical class which acts as an antitussive or cough suppressant and dissociative hallucinogen. It is the dextrorotatory-stereoisomer of racemorphan, the levo-half being levorphanol. Dextrorphan is produced by O-demethylation of dextromethorphan by CYP2D6.
Chemistry[edit]
Dextrorphan is a member of the morphinan class of opioids. It is structurally distinct from the opioids in that it does not contain a double bond in the cyclohexenyl ring. It is also unique among opioids in that it contains a methyl group on the nitrogen atom. This methyl group contributes to its pharmacological properties.
Pharmacology[edit]
Dextrorphan acts as a potent NMDA receptor antagonist, a type of glutamate receptor, which blocks the action of the NMDA receptor, thereby reducing the flow of electrical signals within the brain. This is believed to result in the drug's antitussive effects. Dextrorphan also acts as a sigma-1 receptor agonist, which may contribute to its psychoactive effects.
Medical uses[edit]
Dextrorphan is used as an antitussive, or cough suppressant, in over-the-counter cough and cold medications. It is also used in a clinical setting for its dissociative hallucinogenic effects.
Side effects[edit]
Common side effects of dextrorphan include ataxia, nystagmus, increased heart rate, and hypertension. More serious side effects can include hallucinations, loss of motor control, and psychological dependence.
See also[edit]
-
Dextrorphan
-
Dextrorphane 3D