Prosultiamine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
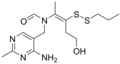
File:Prosultiamine.png|Prosultiamine | |||
File:Prosultiamine_3D_ball.png|Prosultiamine 3D ball | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:52, 17 February 2025
Prosultiamine is a synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1). It is used as a pharmaceutical drug in the treatment of beriberi, a disease caused by thiamine deficiency. Prosultiamine is also used in the treatment of other conditions associated with thiamine deficiency, such as Wernicke's encephalopathy.
Pharmacology[edit]
Prosultiamine is a prodrug of thiamine, meaning it is metabolized in the body to produce thiamine. It is more lipid-soluble than thiamine, allowing it to cross the blood-brain barrier more easily. This makes it more effective in treating conditions affecting the brain, such as Wernicke's encephalopathy.
Clinical uses[edit]
Prosultiamine is used in the treatment of beriberi, a disease caused by thiamine deficiency. Symptoms of beriberi include weight loss, emotional disturbances, impaired sensory perception, weakness and pain in the limbs, and periods of irregular heart rate.
In addition to beriberi, prosultiamine is also used in the treatment of Wernicke's encephalopathy, a serious neurological disorder resulting from thiamine deficiency. This condition is often associated with alcoholism, but can also occur in patients with malnutrition or those who have undergone bariatric surgery.
Side effects[edit]
Like all medications, prosultiamine can cause side effects. These may include allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, or swelling, severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. If any of these effects persist or worsen, patients are advised to tell their doctor or pharmacist promptly.