Toloxatone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
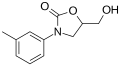
File:Toloxatone.svg|Toloxatone | |||
File:Toloxatone_synthesis.svg|Toloxatone synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:45, 17 February 2025
Toloxatone is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that is used in the treatment of depression. It was introduced in France in 1984 by Théramex, but was later withdrawn from the market due to cases of hepatitis.
Pharmacology[edit]
Toloxatone is a selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), a type of enzyme that breaks down monoamines in the body. By inhibiting MAO-A, toloxatone increases the levels of certain monoamines, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, in the brain. These neurotransmitters are known to play a key role in mood regulation, and their increased availability is thought to alleviate the symptoms of depression.
Medical uses[edit]
Toloxatone is used in the treatment of depression. It is typically prescribed for patients who have not responded to other antidepressant treatments. However, due to its potential side effects, it is usually considered a second-line treatment.
Side effects[edit]
The most common side effects of toloxatone include nausea, dizziness, and insomnia. In rare cases, it can cause more serious side effects, such as hepatitis. Due to these potential risks, patients taking toloxatone are usually closely monitored by their healthcare provider.
History[edit]
Toloxatone was first introduced in France in 1984 by Théramex, a pharmaceutical company. However, it was later withdrawn from the market due to cases of hepatitis associated with its use.