Juxtaoral organ of Chievitz: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[Category:Oral anatomy]] | [[Category:Oral anatomy]] | ||
{{anatomy-stub}} | {{anatomy-stub}} | ||
== Juxtaoral organ of Chievitz == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Juxtaoral_organ_of_Chievitz.100x.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:09, 16 February 2025
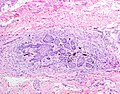
Juxtaoral Organ of Chievitz (JOOC) is a small, anatomically distinct structure located in the buccotemporal fascia, adjacent to the parotid gland and near the masseter muscle. It is a histologically unique entity, characterized by its specialized epithelial cells and surrounding neural tissue. The organ was first described by the Danish anatomist Johan Christian Chievitz in 1885.
Structure[edit]
The Juxtaoral Organ of Chievitz is typically found in the buccotemporal region, embedded within the fascia that envelops the masseter muscle, close to the posterior border of the mandible. It is a microscopic structure, making its in vivo identification challenging. Histologically, it consists of branching cords and nests of epithelial cells surrounded by a dense fibrous stroma. These epithelial cells are thought to be of ectodermal origin, suggesting a developmental relationship with the epidermis.
Function[edit]
The exact function of the Juxtaoral Organ of Chievitz remains largely speculative. Some theories suggest that it may play a role in the sensory innervation of the oral cavity, possibly acting as a mechanoreceptor or proprioceptor. Others propose that it could be involved in the secretion of specific substances, given its structural similarity to other secretory glands. However, due to its small size and the difficulty in studying it, definitive conclusions about its function have not been reached.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The clinical significance of the Juxtaoral Organ of Chievitz is primarily related to its potential involvement in certain pathologies. It can be the site of benign and malignant transformations, although such occurrences are exceedingly rare. Lesions associated with the JOOC, such as cysts or tumors, may present diagnostic challenges due to the organ's obscure nature and the general lack of awareness about it among clinicians.
Histopathology[edit]
Histopathological examination of the Juxtaoral Organ of Chievitz reveals a complex arrangement of epithelial cells, which can sometimes mimic neoplastic processes, leading to diagnostic confusion. The presence of this organ should be considered in the differential diagnosis of orofacial lesions, particularly those arising in the vicinity of the parotid gland and masseter muscle.
Conclusion[edit]
The Juxtaoral Organ of Chievitz is an anatomical and histological curiosity, with its function and clinical relevance still largely unknown. Further research is necessary to elucidate its role within the human body and its significance in disease processes.