Technetium (99mTc) mertiatide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
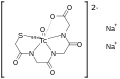
File:Technetium_Tc_99m_mertiatide.svg|Technetium Tc 99m mertiatide | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:09, 16 February 2025
Technetium (99mTc) mertiatide is a radiopharmaceutical agent used in the field of nuclear medicine. It is primarily used for the evaluation of kidney function and to detect potential kidney disorders.
Chemistry[edit]
Technetium (99mTc) mertiatide, also known as 99mTc-MAG3, is a complex of technetium-99m, a metastable nuclear isomer used for its radioactive properties, and mertiatide, a chelating agent. The chelating agent binds to the technetium-99m, allowing it to be safely administered to patients.
Pharmacology[edit]
Once administered, technetium (99mTc) mertiatide is taken up by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. This allows for imaging of the renal system, including the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. The rate of uptake and excretion can provide valuable information about kidney function.
Clinical Use[edit]
Technetium (99mTc) mertiatide is used in renal scintigraphy, a type of medical imaging that provides information about the structure and function of the kidneys. It can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including renal artery stenosis, hydronephrosis, and renal failure. It can also be used to monitor patients who have undergone a kidney transplant.
Safety and Side Effects[edit]
As with any radiopharmaceutical, there is a risk of radiation exposure with the use of technetium (99mTc) mertiatide. However, the amount of radiation is typically low and is considered safe for most patients. Side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions and changes in blood pressure.
See Also[edit]
-
Technetium Tc 99m mertiatide