N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
== N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine == | |||
<gallery> | |||
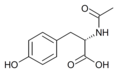
File:Nacetyl-Ltyrosine_structure.png|Structure of N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:53, 16 February 2025
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is a derivative of the amino acid tyrosine. It is often used as a dietary supplement due to its role in the synthesis of protein structures in the body.
Overview[edit]
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine (NALT) is a more soluble form of L-tyrosine, which is an amino acid that's used to produce neurotransmitters. It's often used as a supplement because of its potential benefits for brain health.
Biochemistry[edit]
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is a modified version of the amino acid that's used to synthesize proteins. The acetylation process increases the solubility and absorption of L-tyrosine in the body. This amino acid is a precursor to several important neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
Uses and Benefits[edit]
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is often used as a nootropic, or brain supplement, due to its potential to increase levels of important neurotransmitters in the brain. Some research suggests that it may improve memory, cognition, and mood. However, more research is needed to confirm these potential benefits.
Side Effects and Precautions[edit]
While N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is generally considered safe for most people, it can cause side effects in some cases. These may include nausea, headache, fatigue, and gastrointestinal discomfort. People with certain health conditions, such as those with thyroid disease, should consult with a healthcare provider before taking N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine[edit]
-
Structure of N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine