Ovarian apoplexy: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A medical condition involving the rupture of an ovarian follicle or corpus luteum.}} | |||
== | == Ovarian Apoplexy == | ||
[[File:Ovarian_Apoplexy.svg|thumb|right|Diagram illustrating ovarian apoplexy.]] | |||
'''Ovarian apoplexy''', also known as '''ovarian hemorrhage''', is a medical condition characterized by the rupture of an [[ovarian follicle]] or [[corpus luteum]], leading to bleeding within the [[ovary]]. This condition can cause sudden abdominal pain and may require surgical intervention if the bleeding is severe. | |||
== | == Pathophysiology == | ||
Ovarian apoplexy occurs when there is a rupture of an ovarian structure, such as a follicle or corpus luteum, during the [[menstrual cycle]]. This rupture can lead to bleeding into the ovarian stroma and potentially into the [[peritoneal cavity]]. The bleeding can cause irritation of the peritoneum, leading to acute abdominal pain. | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | |||
Patients with ovarian apoplexy typically present with sudden onset of unilateral lower abdominal pain. The pain may be associated with nausea, vomiting, and sometimes [[syncope]] if the bleeding is significant. On physical examination, there may be tenderness in the lower abdomen, and in severe cases, signs of [[hypovolemic shock]] may be present. | |||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy is primarily clinical, supported by imaging studies. [[Ultrasound]] is the preferred imaging modality and may show free fluid in the pelvis or an enlarged ovary. [[Doppler ultrasound]] can be used to assess blood flow and help differentiate from other causes of acute abdominal pain. | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The management of ovarian apoplexy depends on the severity of the bleeding and the patient's hemodynamic stability. In mild cases, conservative management with analgesics and observation may be sufficient. In cases of significant hemorrhage, surgical intervention, such as [[laparoscopy]] or [[laparotomy]], may be necessary to control the bleeding and repair the ovary. | |||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for ovarian apoplexy is generally good, especially | The prognosis for ovarian apoplexy is generally good, especially with prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. Most women recover fully without long-term complications. However, recurrent episodes can occur, and in rare cases, fertility may be affected if there is significant damage to the ovarian tissue. | ||
== | == Related Pages == | ||
* [[Ovarian cyst]] | * [[Ovarian cyst]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Ectopic pregnancy]] | ||
* [[Pelvic inflammatory disease]] | * [[Pelvic inflammatory disease]] | ||
* [[Acute abdomen]] | |||
[[Category:Gynecological disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Gynecological | |||
Latest revision as of 11:29, 15 February 2025
A medical condition involving the rupture of an ovarian follicle or corpus luteum.
Ovarian Apoplexy[edit]
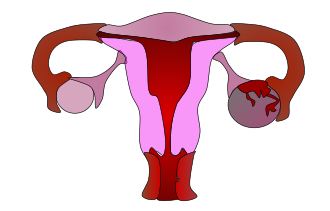
Ovarian apoplexy, also known as ovarian hemorrhage, is a medical condition characterized by the rupture of an ovarian follicle or corpus luteum, leading to bleeding within the ovary. This condition can cause sudden abdominal pain and may require surgical intervention if the bleeding is severe.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Ovarian apoplexy occurs when there is a rupture of an ovarian structure, such as a follicle or corpus luteum, during the menstrual cycle. This rupture can lead to bleeding into the ovarian stroma and potentially into the peritoneal cavity. The bleeding can cause irritation of the peritoneum, leading to acute abdominal pain.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with ovarian apoplexy typically present with sudden onset of unilateral lower abdominal pain. The pain may be associated with nausea, vomiting, and sometimes syncope if the bleeding is significant. On physical examination, there may be tenderness in the lower abdomen, and in severe cases, signs of hypovolemic shock may be present.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy is primarily clinical, supported by imaging studies. Ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality and may show free fluid in the pelvis or an enlarged ovary. Doppler ultrasound can be used to assess blood flow and help differentiate from other causes of acute abdominal pain.
Treatment[edit]
The management of ovarian apoplexy depends on the severity of the bleeding and the patient's hemodynamic stability. In mild cases, conservative management with analgesics and observation may be sufficient. In cases of significant hemorrhage, surgical intervention, such as laparoscopy or laparotomy, may be necessary to control the bleeding and repair the ovary.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for ovarian apoplexy is generally good, especially with prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. Most women recover fully without long-term complications. However, recurrent episodes can occur, and in rare cases, fertility may be affected if there is significant damage to the ovarian tissue.