Propanidid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An intravenous anesthetic agent}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002123 | |||
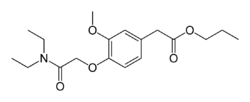
| image = Propanidid-2D-skeletal.png | |||
| image_size = 200px | |||
| image_alt = Skeletal formula of Propanidid | |||
}} | |||
'''Propanidid''' is a short-acting [[intravenous anesthetic]] agent that was used primarily for the induction of [[general anesthesia]]. It is a member of the [[phenylacetate]] class of anesthetics and was introduced in the 1960s. Due to its rapid onset and short duration of action, it was particularly useful in situations requiring quick recovery times. | |||
Propanidid | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Propanidid acts on the [[central nervous system]] to produce a state of unconsciousness. It works by enhancing the activity of the [[gamma-aminobutyric acid]] (GABA) neurotransmitter, which is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. This action results in the depression of the central nervous system, leading to anesthesia. | |||
== | ==Chemical Structure== | ||
[[File:Propanidid-2D-skeletal.png|thumb|left|200px|Skeletal formula of Propanidid]] | |||
Propanidid is chemically classified as an [[ester]] of [[phenylacetic acid]]. Its structure includes a phenyl ring, which is responsible for its lipophilic properties, allowing it to rapidly cross the [[blood-brain barrier]]. | |||
Propanidid | ==Clinical Use== | ||
Propanidid was primarily used for the induction of anesthesia in surgical procedures. Its rapid onset made it suitable for use in [[day surgery]] and other procedures where quick recovery was desired. However, due to the development of newer anesthetics with improved safety profiles, its use has declined. | |||
== Side Effects == | ==Side Effects== | ||
The use of Propanidid was associated with several side effects, including [[hypotension]], [[respiratory depression]], and [[allergic reactions]]. These adverse effects limited its use and led to the development of alternative agents. | |||
==History== | |||
Propanidid was developed in the 1960s and was one of the first intravenous anesthetics to be used clinically. It was marketed under various brand names and was widely used until the 1980s, when it was largely replaced by newer agents such as [[propofol]]. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Anesthesia]] | |||
* [[ | * [[Intravenous therapy]] | ||
* [[General anesthesia]] | |||
* [[Propofol]] | * [[Propofol]] | ||
[[Category:Anesthetics]] | [[Category:Anesthetics]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Phenylacetates]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:19, 15 February 2025
An intravenous anesthetic agent
| Propanidid | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Propanidid is a short-acting intravenous anesthetic agent that was used primarily for the induction of general anesthesia. It is a member of the phenylacetate class of anesthetics and was introduced in the 1960s. Due to its rapid onset and short duration of action, it was particularly useful in situations requiring quick recovery times.
Pharmacology[edit]
Propanidid acts on the central nervous system to produce a state of unconsciousness. It works by enhancing the activity of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter, which is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. This action results in the depression of the central nervous system, leading to anesthesia.
Chemical Structure[edit]

Propanidid is chemically classified as an ester of phenylacetic acid. Its structure includes a phenyl ring, which is responsible for its lipophilic properties, allowing it to rapidly cross the blood-brain barrier.
Clinical Use[edit]
Propanidid was primarily used for the induction of anesthesia in surgical procedures. Its rapid onset made it suitable for use in day surgery and other procedures where quick recovery was desired. However, due to the development of newer anesthetics with improved safety profiles, its use has declined.
Side Effects[edit]
The use of Propanidid was associated with several side effects, including hypotension, respiratory depression, and allergic reactions. These adverse effects limited its use and led to the development of alternative agents.
History[edit]
Propanidid was developed in the 1960s and was one of the first intravenous anesthetics to be used clinically. It was marketed under various brand names and was widely used until the 1980s, when it was largely replaced by newer agents such as propofol.