Submandibular fovea: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Anatomical feature of the human mandible}} | |||
== | ==Submandibular fovea== | ||
The | The '''submandibular fovea''' is a depression located on the medial surface of the [[mandible]], specifically on the body of the mandible. It is an important anatomical feature as it serves as the site for the [[submandibular gland]], one of the major [[salivary glands]] in the human body. | ||
[[File:Gray177.png|thumb|right|Diagram of the mandible showing the submandibular fovea.]] | |||
== | ===Anatomy=== | ||
The submandibular fovea | The submandibular fovea is situated below the [[mylohyoid line]], a ridge on the inner surface of the mandible. It is located near the angle of the mandible, where the body of the mandible meets the [[ramus]]. The fovea provides a shallow depression that accommodates the submandibular gland, allowing it to rest against the bone. | ||
== | ===Function=== | ||
The primary function of the submandibular fovea is to provide a supportive surface for the submandibular gland. This gland is responsible for producing a significant portion of the saliva in the oral cavity, which aids in digestion and oral hygiene. The position of the fovea allows the gland to be in close proximity to the [[oral cavity]], facilitating the secretion of saliva through the [[submandibular duct]]. | |||
[[ | ===Clinical significance=== | ||
[[Category: | Understanding the location and structure of the submandibular fovea is important in various medical fields, including [[dentistry]] and [[oral surgery]]. It is a landmark for surgeons when performing procedures involving the submandibular gland, such as gland excision or treatment of [[sialolithiasis]] (salivary gland stones). Additionally, the fovea's proximity to the [[lingual nerve]] and [[hypoglossal nerve]] is crucial during surgical interventions to avoid nerve damage. | ||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Mandible]] | |||
* [[Submandibular gland]] | |||
* [[Salivary gland]] | |||
* [[Mylohyoid line]] | |||
[[Category:Anatomy of the human head and neck]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 15 February 2025
Anatomical feature of the human mandible
Submandibular fovea[edit]
The submandibular fovea is a depression located on the medial surface of the mandible, specifically on the body of the mandible. It is an important anatomical feature as it serves as the site for the submandibular gland, one of the major salivary glands in the human body.
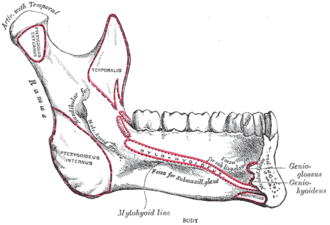
Anatomy[edit]
The submandibular fovea is situated below the mylohyoid line, a ridge on the inner surface of the mandible. It is located near the angle of the mandible, where the body of the mandible meets the ramus. The fovea provides a shallow depression that accommodates the submandibular gland, allowing it to rest against the bone.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the submandibular fovea is to provide a supportive surface for the submandibular gland. This gland is responsible for producing a significant portion of the saliva in the oral cavity, which aids in digestion and oral hygiene. The position of the fovea allows the gland to be in close proximity to the oral cavity, facilitating the secretion of saliva through the submandibular duct.
Clinical significance[edit]
Understanding the location and structure of the submandibular fovea is important in various medical fields, including dentistry and oral surgery. It is a landmark for surgeons when performing procedures involving the submandibular gland, such as gland excision or treatment of sialolithiasis (salivary gland stones). Additionally, the fovea's proximity to the lingual nerve and hypoglossal nerve is crucial during surgical interventions to avoid nerve damage.