Trigeminal nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Trigeminal Nerve == | |||
The '''trigeminal nerve''' is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V) and is responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is the largest of the cranial nerves and has both sensory and motor components. | |||
The '''trigeminal nerve''' | |||
=== | === Anatomy === | ||
The trigeminal nerve originates from the brainstem, specifically from the pons. It has three major branches: | |||
The | |||
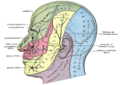
* The [[Ophthalmic nerve]] (V1) is purely sensory and supplies the forehead, scalp, and upper eyelids. | |||
The [[ | * The [[Maxillary nerve]] (V2) is also sensory and supplies the lower eyelids, cheeks, nostrils, upper lip, and upper gum. | ||
* The [[Mandibular nerve]] (V3) has both sensory and motor functions. It supplies the lower lip, lower gum, chin, and also controls the muscles of mastication. | |||
== Clinical | === Function === | ||
The trigeminal nerve is primarily responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain. It also controls the muscles involved in chewing. The sensory functions include touch, pain, and temperature sensations from the face. | |||
=== Clinical Significance === | |||
Disorders of the trigeminal nerve can lead to conditions such as [[trigeminal neuralgia]], which is characterized by severe facial pain. Other conditions include loss of sensation or motor function in the areas supplied by the nerve. | |||
=== Related Structures === | |||
The [[trigeminal ganglion]] is a collection of nerve cell bodies of the trigeminal nerve located in the skull. It is the site where the sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve converge. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Cranial nerves]] | * [[Cranial nerves]] | ||
* [[Trigeminal neuralgia]] | |||
* [[Facial nerve]] | * [[Facial nerve]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* Standring, S. (2016). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st Edition. Elsevier. | |||
* "Trigeminal Nerve." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trigeminal_nerve | |||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Grant_1962_654.png|Diagram of the trigeminal nerve | |||
File:Brain_human_normal_inferior_view_with_labels_en.svg|Inferior view of the human brain | |||
File:Gray784.png|Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve | |||
File:Trig_innervation.svg|Innervation areas of the trigeminal nerve | |||
File:Sensory_Pathways_III.png|Sensory pathways of the trigeminal nerve | |||
File:Touch_Pain_Pathways.png|Touch and pain pathways | |||
File:Gray696_Trigeminal.svg|Trigeminal nerve anatomy | |||
File:Onionskinddistribution.svg|Onion skin distribution of trigeminal nerve | |||
File:Sensory_Homunculus.png|Sensory homunculus | |||
File:Grant_1962_655.png|Trigeminal nerve branches | |||
File:Grant_1962_656a.png|Trigeminal nerve sensory distribution | |||
File:Grant_1962_656b.png|Trigeminal nerve motor distribution | |||
File:Grant_1962_470.png|Trigeminal nerve in the brain | |||
File:Gray778_Trigeminal.png|Trigeminal nerve pathways | |||
File:Trigeminal_ganglion.jpg|Trigeminal ganglion | |||
File:Slide2cuc.JPG|Trigeminal nerve in cross-section | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | |||
Revision as of 00:41, 10 February 2025
Trigeminal Nerve
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V) and is responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is the largest of the cranial nerves and has both sensory and motor components.
Anatomy
The trigeminal nerve originates from the brainstem, specifically from the pons. It has three major branches:
- The Ophthalmic nerve (V1) is purely sensory and supplies the forehead, scalp, and upper eyelids.
- The Maxillary nerve (V2) is also sensory and supplies the lower eyelids, cheeks, nostrils, upper lip, and upper gum.
- The Mandibular nerve (V3) has both sensory and motor functions. It supplies the lower lip, lower gum, chin, and also controls the muscles of mastication.
Function
The trigeminal nerve is primarily responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain. It also controls the muscles involved in chewing. The sensory functions include touch, pain, and temperature sensations from the face.
Clinical Significance
Disorders of the trigeminal nerve can lead to conditions such as trigeminal neuralgia, which is characterized by severe facial pain. Other conditions include loss of sensation or motor function in the areas supplied by the nerve.
Related Structures
The trigeminal ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies of the trigeminal nerve located in the skull. It is the site where the sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve converge.
Related Pages
References
- Standring, S. (2016). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st Edition. Elsevier.
- "Trigeminal Nerve." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trigeminal_nerve
Gallery
-
Diagram of the trigeminal nerve
-
Inferior view of the human brain
-
Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve
-
Innervation areas of the trigeminal nerve
-
Sensory pathways of the trigeminal nerve
-
Touch and pain pathways
-
Trigeminal nerve anatomy
-
Onion skin distribution of trigeminal nerve
-
Sensory homunculus
-
Trigeminal nerve branches
-
Trigeminal nerve sensory distribution
-
Trigeminal nerve motor distribution
-
Trigeminal nerve in the brain
-
Trigeminal nerve pathways
-
Trigeminal ganglion
-
Trigeminal nerve in cross-section