Strategic management: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | [[File:Strategic management tools.png|thumb]] [[File:Strategic Management Framework.png|thumb]] [[File:SWOT en.svg|thumb]] [[File:Experience curve.gif|thumb]] Strategic Management | ||
Strategic management is a comprehensive and ongoing management process aimed at formulating and implementing effective strategies to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It involves the analysis of internal and external environments, the formulation of strategies, the implementation of these strategies, and the evaluation of their effectiveness. | |||
Strategic management | |||
== | ==Overview== | ||
Strategic management is essential for organizations to navigate complex and dynamic environments. It provides a framework for aligning resources and capabilities with the external opportunities and threats. The process is typically divided into several key stages: | |||
== | ===1. Environmental Scanning=== | ||
Environmental scanning involves the systematic collection and analysis of information about the internal and external environments of an organization. This includes: | |||
* '''Internal Analysis''': Assessing the organization's resources, capabilities, and core competencies. | |||
* '''External Analysis''': Examining the industry environment, including competitors, market trends, and regulatory factors. | |||
* | |||
== | ===2. Strategy Formulation=== | ||
Strategy formulation is the process of deciding the best course of action for achieving organizational objectives. It involves: | |||
* '''Setting Objectives''': Defining clear, measurable, and achievable goals. | |||
* | * '''Developing Strategies''': Creating plans to leverage strengths and opportunities while mitigating weaknesses and threats. | ||
* | |||
== | ===3. Strategy Implementation=== | ||
Strategy implementation involves putting the formulated strategies into action. This requires: | |||
* '''Resource Allocation''': Distributing resources effectively to support strategic initiatives. | |||
* '''Organizational Change''': Adjusting organizational structures and processes to facilitate strategy execution. | |||
===4. Strategy Evaluation=== | |||
Strategy evaluation is the final stage, where the effectiveness of the strategy is assessed. This includes: | |||
{{ | * '''Performance Measurement''': Using key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. | ||
* '''Feedback and Control''': Making necessary adjustments based on performance data. | |||
==Key Concepts== | |||
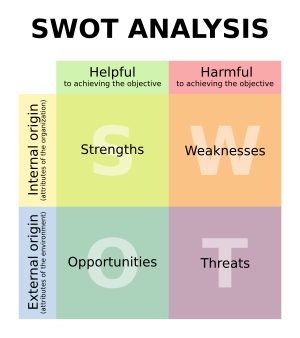
===SWOT Analysis=== | |||
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a business or project. It helps in understanding the internal and external factors that can impact strategic decisions. | |||
===Porter's Five Forces=== | |||
Porter's Five Forces is a framework for analyzing the competitive forces within an industry. It includes: | |||
* '''Threat of New Entrants''' | |||
* '''Bargaining Power of Suppliers''' | |||
* '''Bargaining Power of Buyers''' | |||
* '''Threat of Substitute Products or Services''' | |||
* '''Industry Rivalry''' | |||
===Balanced Scorecard=== | |||
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive view of an organization's performance by measuring financial and non-financial metrics across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. | |||
==Importance of Strategic Management== | |||
Strategic management is crucial for: | |||
* '''Long-term Success''': Ensuring the organization remains competitive and sustainable over time. | |||
* '''Adaptability''': Enabling organizations to respond effectively to changes in the external environment. | |||
* '''Resource Optimization''': Ensuring resources are used efficiently to achieve strategic goals. | |||
==Challenges in Strategic Management== | |||
Some common challenges include: | |||
* '''Rapid Technological Changes''': Keeping up with technological advancements that can disrupt industries. | |||
* '''Globalization''': Managing the complexities of operating in a global market. | |||
* '''Organizational Resistance''': Overcoming resistance to change within the organization. | |||
==Also see== | |||
* [[Business Strategy]] | |||
* [[Corporate Governance]] | |||
* [[Organizational Behavior]] | |||
* [[Change Management]] | |||
{{Strategic Management}} | |||
[[Category:Business Management]] | |||
[[Category:Strategic Planning]] | |||
Revision as of 15:42, 9 December 2024


Strategic Management
Strategic management is a comprehensive and ongoing management process aimed at formulating and implementing effective strategies to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It involves the analysis of internal and external environments, the formulation of strategies, the implementation of these strategies, and the evaluation of their effectiveness.
Overview
Strategic management is essential for organizations to navigate complex and dynamic environments. It provides a framework for aligning resources and capabilities with the external opportunities and threats. The process is typically divided into several key stages:
1. Environmental Scanning
Environmental scanning involves the systematic collection and analysis of information about the internal and external environments of an organization. This includes:
- Internal Analysis: Assessing the organization's resources, capabilities, and core competencies.
- External Analysis: Examining the industry environment, including competitors, market trends, and regulatory factors.
2. Strategy Formulation
Strategy formulation is the process of deciding the best course of action for achieving organizational objectives. It involves:
- Setting Objectives: Defining clear, measurable, and achievable goals.
- Developing Strategies: Creating plans to leverage strengths and opportunities while mitigating weaknesses and threats.
3. Strategy Implementation
Strategy implementation involves putting the formulated strategies into action. This requires:
- Resource Allocation: Distributing resources effectively to support strategic initiatives.
- Organizational Change: Adjusting organizational structures and processes to facilitate strategy execution.
4. Strategy Evaluation
Strategy evaluation is the final stage, where the effectiveness of the strategy is assessed. This includes:
- Performance Measurement: Using key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress.
- Feedback and Control: Making necessary adjustments based on performance data.
Key Concepts
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a business or project. It helps in understanding the internal and external factors that can impact strategic decisions.
Porter's Five Forces
Porter's Five Forces is a framework for analyzing the competitive forces within an industry. It includes:
- Threat of New Entrants
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Threat of Substitute Products or Services
- Industry Rivalry
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive view of an organization's performance by measuring financial and non-financial metrics across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Importance of Strategic Management
Strategic management is crucial for:
- Long-term Success: Ensuring the organization remains competitive and sustainable over time.
- Adaptability: Enabling organizations to respond effectively to changes in the external environment.
- Resource Optimization: Ensuring resources are used efficiently to achieve strategic goals.
Challenges in Strategic Management
Some common challenges include:
- Rapid Technological Changes: Keeping up with technological advancements that can disrupt industries.
- Globalization: Managing the complexities of operating in a global market.
- Organizational Resistance: Overcoming resistance to change within the organization.