Shoulder impingement syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Shoulder impingement syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Shoulder_joint.svg|Diagram of the shoulder joint]] | |||
| caption = Diagram of the shoulder joint | |||
| synonyms = Subacromial impingement, painful arc syndrome, supraspinatus syndrome, swimmer's shoulder, thrower's shoulder | |||
| specialty = [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Shoulder pain]], [[weakness]], [[reduced range of motion]] | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Repetitive overhead activity]], [[shoulder instability]], [[muscle imbalance]] | |||
| risks = [[Athletic activities]], [[occupational hazards]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Rotator cuff tear]], [[adhesive capsulitis]], [[bursitis]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[NSAIDs]], [[corticosteroid injections]], [[surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in athletes and manual laborers | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Flat acromion.jpg|left|thumb|Flat acromion]] | |||
[[File:Curved acromion.jpg|left|thumb|Curved acromion]] | |||
[[File:Hooked acromion.jpg|left|thumb|Hooked acromion]] | |||
[[File:MRI. Subacromial impingement..jpg|thumb|MRI of Subacromial impingement]] | |||
'''Shoulder Impingement Syndrome''' is a common condition affecting the shoulder joint. It is also known as [[Subacromial Impingement]], [[Swimmer's Shoulder]], [[Thrower's Shoulder]], and [[Painful Arc Syndrome]]. | '''Shoulder Impingement Syndrome''' is a common condition affecting the shoulder joint. It is also known as [[Subacromial Impingement]], [[Swimmer's Shoulder]], [[Thrower's Shoulder]], and [[Painful Arc Syndrome]]. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is caused by the tendons of the [[rotator cuff]] muscles becoming impinged as they pass through a narrow bony space in the shoulder called the [[subacromial space]]. This can cause pain, weakness and loss of movement at the shoulder. | Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is caused by the tendons of the [[rotator cuff]] muscles becoming impinged as they pass through a narrow bony space in the shoulder called the [[subacromial space]]. This can cause pain, weakness and loss of movement at the shoulder. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The main symptoms of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome include: | The main symptoms of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome include: | ||
| Line 11: | Line 31: | ||
* Difficulty lifting objects, especially overhead. | * Difficulty lifting objects, especially overhead. | ||
* [[Pain at night]], which can affect sleep. | * [[Pain at night]], which can affect sleep. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is usually made based on the symptoms and a physical examination. However, further tests such as an [[X-ray]], [[MRI]] or [[Ultrasound]] may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. | The diagnosis of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is usually made based on the symptoms and a physical examination. However, further tests such as an [[X-ray]], [[MRI]] or [[Ultrasound]] may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for Shoulder Impingement Syndrome usually involves a combination of rest, [[physiotherapy]], pain relief and sometimes [[surgery]]. The aim of treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation, and to restore normal function to the shoulder. | Treatment for Shoulder Impingement Syndrome usually involves a combination of rest, [[physiotherapy]], pain relief and sometimes [[surgery]]. The aim of treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation, and to restore normal function to the shoulder. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Prevention of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome can often be achieved through regular [[exercise]] to strengthen the shoulder muscles, good posture, and avoiding activities that cause pain. | Prevention of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome can often be achieved through regular [[exercise]] to strengthen the shoulder muscles, good posture, and avoiding activities that cause pain. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Rotator Cuff]] | * [[Rotator Cuff]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Frozen Shoulder]] | * [[Frozen Shoulder]] | ||
* [[Shoulder Arthritis]] | * [[Shoulder Arthritis]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
[[Category:Physical Therapy]] | [[Category:Physical Therapy]] | ||
[[Category:Sports Medicine]] | [[Category:Sports Medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Rheumatology]] | [[Category:Rheumatology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:27, 13 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Shoulder impingement syndrome | |
|---|---|
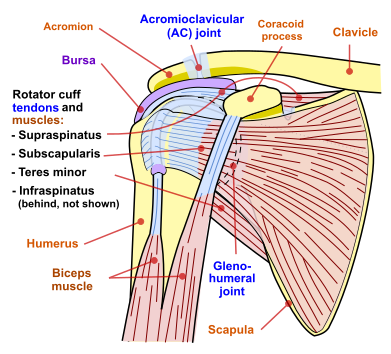
| |
| Synonyms | Subacromial impingement, painful arc syndrome, supraspinatus syndrome, swimmer's shoulder, thrower's shoulder |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Orthopedics |
| Symptoms | Shoulder pain, weakness, reduced range of motion |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Repetitive overhead activity, shoulder instability, muscle imbalance |
| Risks | Athletic activities, occupational hazards |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Rotator cuff tear, adhesive capsulitis, bursitis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in athletes and manual laborers |
| Deaths | N/A |




Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is a common condition affecting the shoulder joint. It is also known as Subacromial Impingement, Swimmer's Shoulder, Thrower's Shoulder, and Painful Arc Syndrome.
Causes[edit]
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is caused by the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles becoming impinged as they pass through a narrow bony space in the shoulder called the subacromial space. This can cause pain, weakness and loss of movement at the shoulder.
Symptoms[edit]
The main symptoms of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome include:
- Pain in the shoulder and arm, which may be worse when lifting the arm, lying on it or during activities that require reaching overhead.
- Weakness of the shoulder muscles.
- Stiffness in the shoulder.
- Difficulty lifting objects, especially overhead.
- Pain at night, which can affect sleep.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome is usually made based on the symptoms and a physical examination. However, further tests such as an X-ray, MRI or Ultrasound may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for Shoulder Impingement Syndrome usually involves a combination of rest, physiotherapy, pain relief and sometimes surgery. The aim of treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation, and to restore normal function to the shoulder.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome can often be achieved through regular exercise to strengthen the shoulder muscles, good posture, and avoiding activities that cause pain.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />


