Human: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Lucy_Skeleton.jpg|Lucy skeleton|thumb]] | |||
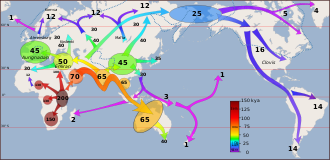
[[File:Early_migrations_mercator.svg|Early human migrations|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Cleric-Knight-Workman.jpg|Cleric-Knight-Workman|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Maquina_vapor_Watt_ETSIIM.jpg|Maquina vapor Watt|thumb]] | |||
The '''human''' species, scientifically known as ''Homo sapiens'', is a bipedal primate characterized by its advanced cognitive abilities, including complex language use, problem-solving, and social structures. Humans are unique in their ability to alter their environment with technology, a trait that has allowed them to inhabit various ecosystems across the globe. | The '''human''' species, scientifically known as ''Homo sapiens'', is a bipedal primate characterized by its advanced cognitive abilities, including complex language use, problem-solving, and social structures. Humans are unique in their ability to alter their environment with technology, a trait that has allowed them to inhabit various ecosystems across the globe. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
Humans have developed technology to manipulate their environment, from the creation of simple tools to the development of agriculture, cities, and advanced digital technology. This ability to create and use technology is a significant factor in humans' ability to adapt to and change their environments. | Humans have developed technology to manipulate their environment, from the creation of simple tools to the development of agriculture, cities, and advanced digital technology. This ability to create and use technology is a significant factor in humans' ability to adapt to and change their environments. | ||
== | == Gallery == | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Population_Density,_v4.11,_2020_(48009093621).jpg|Human population dentistry | |||
File:Distribution-of-earths-mammals.png|Distribution-of-earths-mammals | |||
File:Anterior_view_of_human_female_and_male,_with_labels_2.png|Anterior_view_of_human_female_and_male | |||
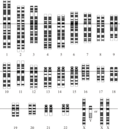
File:Karyotype.png|Human Karyotype | |||
File:Tubal_Pregnancy_with_embryo.jpg|Tubal_Pregnancy_with_embryo | |||
File:Redheaded_child_mesmerized_2.jpg|Redheaded_child_mesmerized | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category:Humans]] | [[Category:Humans]] | ||
[[Category:Anthropology]] | [[Category:Anthropology]] | ||
[[Category:Biology]] | [[Category:Biology]] | ||
{{ | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:10, 21 March 2025

The human species, scientifically known as Homo sapiens, is a bipedal primate characterized by its advanced cognitive abilities, including complex language use, problem-solving, and social structures. Humans are unique in their ability to alter their environment with technology, a trait that has allowed them to inhabit various ecosystems across the globe.
Evolution[edit]
Humans are part of the family Hominidae, which includes the great apes. The evolutionary path of humans diverged from that of chimpanzees and bonobos, our closest living relatives, approximately 5 to 7 million years ago. The genus Homo evolved in Africa, with the species Homo sapiens emerging around 300,000 years ago. Early humans developed tools, controlled fire, and eventually spread out of Africa, adapting to a wide range of environments.
Anatomy and Physiology[edit]
Human anatomy is characterized by an upright posture, with two legs that facilitate bipedal locomotion and two arms capable of manipulating objects and using tools. The human brain is notable for its size and complexity, enabling advanced abstract reasoning, language, introspection, and problem-solving.
Skeletal System[edit]
The human skeletal system provides support and protection for the body's organs and structures, enables movement by attaching muscles, and stores minerals. It consists of 206 bones in the adult body, divided into the axial skeleton (which includes the skull and vertebral column) and the appendicular skeleton (which includes the limbs and girdles).
Muscular System[edit]
The human muscular system is responsible for movement and posture. It comprises over 600 muscles, which work in pairs to contract and relax, pulling on bones of the skeletal system to facilitate movement.
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems[edit]
The circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removes carbon dioxide and waste products. The heart pumps blood through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. The respiratory system, consisting of the lungs and airways, facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and blood.
Nervous System[edit]
The nervous system controls both voluntary actions, like movement, and involuntary actions, like breathing. It comprises the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves that extend throughout the body. The human brain is the center of consciousness, thought, memory, and emotion.
Culture and Society[edit]
Humans are inherently social beings, with cultures that have evolved complex systems of values, morals, laws, and customs. Language, art, music, and literature are significant aspects of human culture, allowing for the expression of ideas, emotions, and history.
Language[edit]
Language is a defining characteristic of the human species. It allows for the communication of complex ideas, emotions, and instructions. Humans use spoken languages, sign languages, and written languages to communicate with one another.
Technology[edit]
Humans have developed technology to manipulate their environment, from the creation of simple tools to the development of agriculture, cities, and advanced digital technology. This ability to create and use technology is a significant factor in humans' ability to adapt to and change their environments.
Gallery[edit]
-
Human population dentistry
-
Distribution-of-earths-mammals
-
Anterior_view_of_human_female_and_male
-
Human Karyotype
-
Tubal_Pregnancy_with_embryo
-
Redheaded_child_mesmerized