Wellens' syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Wellens' syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Wellens'_Syndrome.png|250px]] | |||
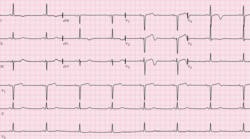
| caption = Electrocardiogram showing Wellens' syndrome | |||
| synonyms = LAD coronary T-wave syndrome | |||
| pronounce = | |||
| specialty = [[Cardiology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Chest pain]], [[T-wave inversion]] in [[ECG]] | |||
| complications = [[Myocardial infarction]] | |||
| onset = | |||
| duration = | |||
| types = Type A, Type B | |||
| causes = [[Coronary artery disease]] | |||
| risks = | |||
| diagnosis = [[Electrocardiogram]], [[Cardiac catheterization]] | |||
| differential = | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = [[Percutaneous coronary intervention]], [[Coronary artery bypass surgery]] | |||
| medication = | |||
| prognosis = High risk of [[myocardial infarction]] if untreated | |||
| frequency = | |||
| deaths = | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Wellens'_Warning.gif|Wellens' warning|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:WellensPain.JPG|Wellens' syndrome|thumb]] | |||
[[File:WellensPainfree.JPG|Wellens' syndrome|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Wellens' syndrome''' is a pattern of [[Electrocardiography|ECG]] changes associated with critical stenosis of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending coronary artery]], which can progress to an extensive [[Anterior wall myocardial infarction|anterior wall myocardial infarction]] if not recognized and treated appropriately. It is named after Hein J.J. Wellens, a Dutch cardiologist who first described the syndrome in 1982. | '''Wellens' syndrome''' is a pattern of [[Electrocardiography|ECG]] changes associated with critical stenosis of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending coronary artery]], which can progress to an extensive [[Anterior wall myocardial infarction|anterior wall myocardial infarction]] if not recognized and treated appropriately. It is named after Hein J.J. Wellens, a Dutch cardiologist who first described the syndrome in 1982. | ||
==Clinical Presentation== | ==Clinical Presentation== | ||
Patients with Wellens' syndrome typically present with a history of angina, often with a recent increase in frequency or severity. The pain is usually described as a heavy or squeezing sensation in the chest, often radiating to the left arm or jaw. On examination, the patient may appear anxious and sweaty, but is often comfortable at rest. | Patients with Wellens' syndrome typically present with a history of angina, often with a recent increase in frequency or severity. The pain is usually described as a heavy or squeezing sensation in the chest, often radiating to the left arm or jaw. On examination, the patient may appear anxious and sweaty, but is often comfortable at rest. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis of Wellens' syndrome is made on the basis of the characteristic ECG changes, which include deep, symmetric [[T wave]] inversions in the anterior leads (V1-V4). These changes are typically present during pain-free periods and may be transient, reverting to normal between episodes of pain. Other diagnostic criteria include the absence of significant [[ST segment]] elevation and the absence of [[pathologic Q wave]]s. | The diagnosis of Wellens' syndrome is made on the basis of the characteristic ECG changes, which include deep, symmetric [[T wave]] inversions in the anterior leads (V1-V4). These changes are typically present during pain-free periods and may be transient, reverting to normal between episodes of pain. Other diagnostic criteria include the absence of significant [[ST segment]] elevation and the absence of [[pathologic Q wave]]s. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment of Wellens' syndrome involves urgent coronary angiography to identify the site of the critical stenosis, followed by revascularization, usually by means of [[Percutaneous coronary intervention|percutaneous coronary intervention]] (PCI). Medical management with [[antiplatelet therapy]], [[beta blockers]], and [[statins]] is also important. | The treatment of Wellens' syndrome involves urgent coronary angiography to identify the site of the critical stenosis, followed by revascularization, usually by means of [[Percutaneous coronary intervention|percutaneous coronary intervention]] (PCI). Medical management with [[antiplatelet therapy]], [[beta blockers]], and [[statins]] is also important. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis of Wellens' syndrome is poor if left untreated, with a high risk of progression to extensive anterior wall myocardial infarction. However, with early recognition and appropriate treatment, the prognosis can be significantly improved. | The prognosis of Wellens' syndrome is poor if left untreated, with a high risk of progression to extensive anterior wall myocardial infarction. However, with early recognition and appropriate treatment, the prognosis can be significantly improved. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Electrocardiography]] | * [[Electrocardiography]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 46: | ||
* [[Beta blockers]] | * [[Beta blockers]] | ||
* [[Statins]] | * [[Statins]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Medical syndromes]] | [[Category:Medical syndromes]] | ||
[[Category:ECG]] | [[Category:ECG]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:05, 13 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Wellens' syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | LAD coronary T-wave syndrome |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, T-wave inversion in ECG |
| Complications | Myocardial infarction |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | Type A, Type B |
| Causes | Coronary artery disease |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Electrocardiogram, Cardiac catheterization |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Percutaneous coronary intervention, Coronary artery bypass surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | High risk of myocardial infarction if untreated |
| Frequency | |
| Deaths | |



Wellens' syndrome is a pattern of ECG changes associated with critical stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery, which can progress to an extensive anterior wall myocardial infarction if not recognized and treated appropriately. It is named after Hein J.J. Wellens, a Dutch cardiologist who first described the syndrome in 1982.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with Wellens' syndrome typically present with a history of angina, often with a recent increase in frequency or severity. The pain is usually described as a heavy or squeezing sensation in the chest, often radiating to the left arm or jaw. On examination, the patient may appear anxious and sweaty, but is often comfortable at rest.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of Wellens' syndrome is made on the basis of the characteristic ECG changes, which include deep, symmetric T wave inversions in the anterior leads (V1-V4). These changes are typically present during pain-free periods and may be transient, reverting to normal between episodes of pain. Other diagnostic criteria include the absence of significant ST segment elevation and the absence of pathologic Q waves.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of Wellens' syndrome involves urgent coronary angiography to identify the site of the critical stenosis, followed by revascularization, usually by means of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Medical management with antiplatelet therapy, beta blockers, and statins is also important.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis of Wellens' syndrome is poor if left untreated, with a high risk of progression to extensive anterior wall myocardial infarction. However, with early recognition and appropriate treatment, the prognosis can be significantly improved.


