Buccal space: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
File:Gray176.png|Buccal space cross-section | File:Gray176.png|Buccal space cross-section | ||
File:Abces_dentaire.jpg|Dental abscess in the buccal space | File:Abces_dentaire.jpg|Dental abscess in the buccal space | ||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray380.png|Buccal space | |||
File:Gray157.png|Buccal space | |||
File:Gray176.png|Buccal space | |||
File:Abces_dentaire.jpg|Buccal space | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 04:39, 18 February 2025
Buccal Space
The Buccal Space is an anatomical region in the human body, specifically located in the head and neck region. It is a potential space in the face and is paired on either side. The buccal space is part of the deep facial spaces.
Anatomy
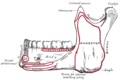
The buccal space is bordered by the buccinator muscle medially, and the masseter muscle laterally. Superiorly, it is limited by the zygomaticus muscle and the zygomatic arch, and inferiorly by the mandible. Anteriorly, it is limited by the orbicularis oris muscle and posteriorly by the pterygomandibular raphe and the superior constrictor muscle of the pharynx.
Clinical Significance
The buccal space is clinically significant as it is a potential space for the spread of infections and tumors. Infections in the buccal space can lead to buccal space abscess, which is a collection of pus in the buccal space. This can cause swelling, pain, and difficulty in opening the mouth.
Treatment
Treatment of buccal space abscess involves drainage of the abscess and antibiotics. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required.