Pneumonic plague: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Pneumonic plague | |||
| image = [[File:Yersinia_pestis.jpg|alt=Yersinia pestis|upright=1.2]] | |||
| caption = ''[[Yersinia pestis]]'', the bacterium that causes pneumonic plague | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Fever]], [[headache]], [[weakness]], [[cough]], [[shortness of breath]], [[chest pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Respiratory failure]], [[septic shock]], [[death]] | |||
| onset = 1 to 7 days after exposure | |||
| duration = Varies, can be fatal within 24 hours if untreated | |||
| causes = ''[[Yersinia pestis]]'' | |||
| risks = Contact with infected animals or humans, [[bioterrorism]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Culture (microbiology)|Culture]], [[polymerase chain reaction|PCR]], [[serology]] | |||
| differential = [[Pneumonia]], [[tuberculosis]], [[influenza]] | |||
| prevention = Avoiding contact with infected individuals, [[prophylactic antibiotics]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antibiotics]] such as [[streptomycin]], [[gentamicin]], [[doxycycline]], [[ciprofloxacin]] | |||
| prognosis = High mortality if untreated, better with early treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = High mortality rate if untreated | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Medical_team_working_together_during_the_plague_period_in_Madagascar.jpg|Medical team working together during the plague period in Madagascar|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Pneumonic plague''' is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium ''[[Yersinia pestis]]''. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is one of three forms of plague, the other two being [[septicemic plague]] and [[bubonic plague]]. | '''Pneumonic plague''' is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium ''[[Yersinia pestis]]''. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is one of three forms of plague, the other two being [[septicemic plague]] and [[bubonic plague]]. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The cause of pneumonic plague is ''Yersinia pestis'', a gram-negative bacterium. The bacteria are usually transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected [[flea]]. However, pneumonic plague can also be transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets. | The cause of pneumonic plague is ''Yersinia pestis'', a gram-negative bacterium. The bacteria are usually transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected [[flea]]. However, pneumonic plague can also be transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of pneumonic plague typically begin within a few days of exposure to the bacteria. They include fever, headache, weakness, and rapidly developing pneumonia with shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, and sometimes bloody or watery sputum. | Symptoms of pneumonic plague typically begin within a few days of exposure to the bacteria. They include fever, headache, weakness, and rapidly developing pneumonia with shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, and sometimes bloody or watery sputum. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of pneumonic plague can be challenging due to its rarity and the commonality of its symptoms with other conditions. However, it can be confirmed through laboratory tests such as blood cultures or sputum cultures. | Diagnosis of pneumonic plague can be challenging due to its rarity and the commonality of its symptoms with other conditions. However, it can be confirmed through laboratory tests such as blood cultures or sputum cultures. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Pneumonic plague is a serious illness and requires immediate medical attention. Treatment typically involves antibiotics such as [[streptomycin]], [[gentamicin]], or [[doxycycline]]. If left untreated, pneumonic plague can be fatal. | Pneumonic plague is a serious illness and requires immediate medical attention. Treatment typically involves antibiotics such as [[streptomycin]], [[gentamicin]], or [[doxycycline]]. If left untreated, pneumonic plague can be fatal. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Prevention of pneumonic plague involves avoiding contact with infected animals and taking precautions to prevent flea bites. In some cases, prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended. | Prevention of pneumonic plague involves avoiding contact with infected animals and taking precautions to prevent flea bites. In some cases, prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Black Death]] | * [[Black Death]] | ||
* [[Plague of Justinian]] | * [[Plague of Justinian]] | ||
* [[Third plague pandemic]] | * [[Third plague pandemic]] | ||
[[Category:Infectious diseases]] | [[Category:Infectious diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | [[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Zoonotic diseases]] | [[Category:Zoonotic diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:41, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Pneumonic plague | |
|---|---|
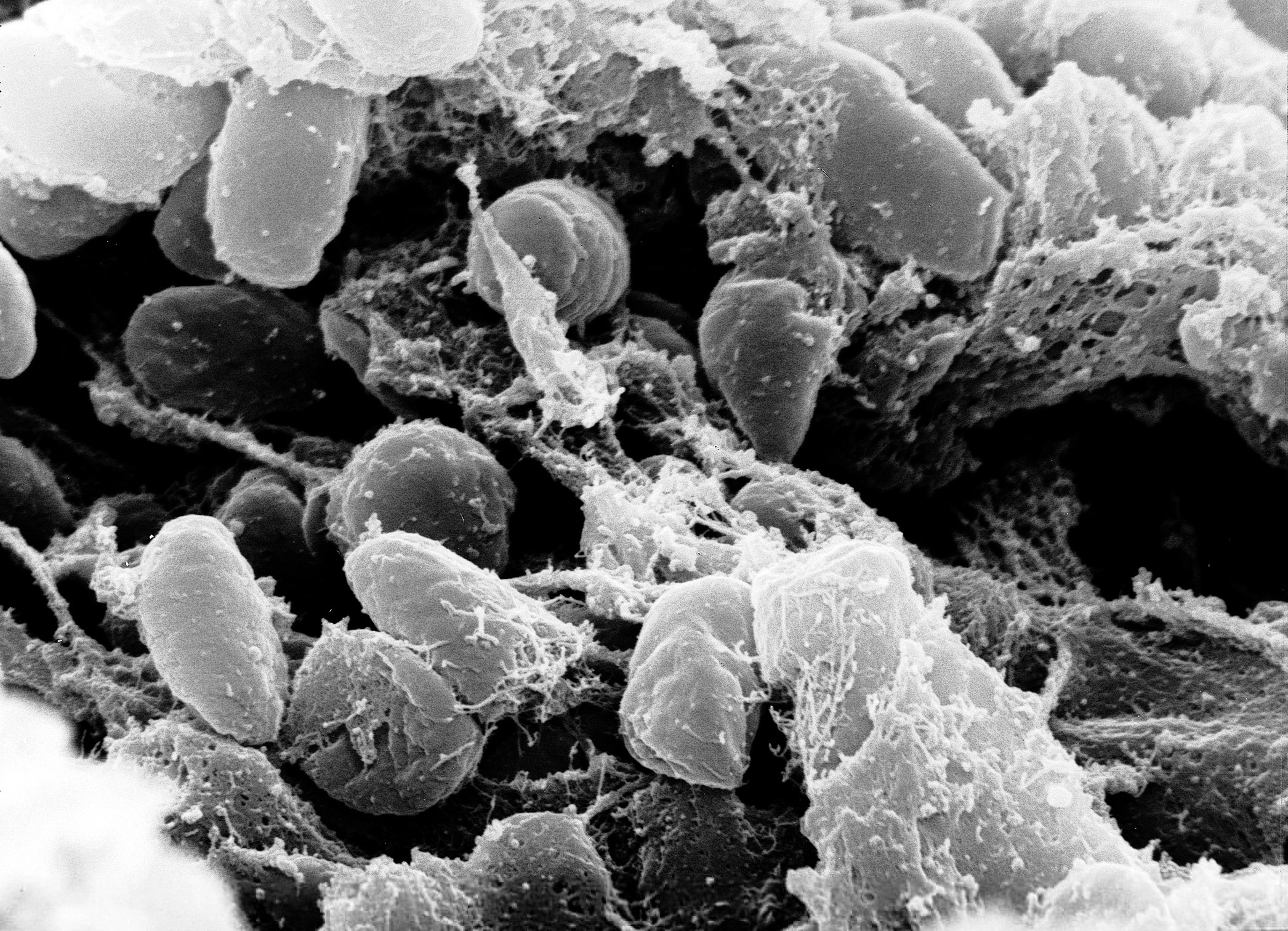
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fever, headache, weakness, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Complications | Respiratory failure, septic shock, death |
| Onset | 1 to 7 days after exposure |
| Duration | Varies, can be fatal within 24 hours if untreated |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Yersinia pestis |
| Risks | Contact with infected animals or humans, bioterrorism |
| Diagnosis | Culture, PCR, serology |
| Differential diagnosis | Pneumonia, tuberculosis, influenza |
| Prevention | Avoiding contact with infected individuals, prophylactic antibiotics |
| Treatment | Antibiotics such as streptomycin, gentamicin, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | High mortality if untreated, better with early treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | High mortality rate if untreated |

Pneumonic plague is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is one of three forms of plague, the other two being septicemic plague and bubonic plague.
Causes[edit]
The cause of pneumonic plague is Yersinia pestis, a gram-negative bacterium. The bacteria are usually transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected flea. However, pneumonic plague can also be transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of pneumonic plague typically begin within a few days of exposure to the bacteria. They include fever, headache, weakness, and rapidly developing pneumonia with shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, and sometimes bloody or watery sputum.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of pneumonic plague can be challenging due to its rarity and the commonality of its symptoms with other conditions. However, it can be confirmed through laboratory tests such as blood cultures or sputum cultures.
Treatment[edit]
Pneumonic plague is a serious illness and requires immediate medical attention. Treatment typically involves antibiotics such as streptomycin, gentamicin, or doxycycline. If left untreated, pneumonic plague can be fatal.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of pneumonic plague involves avoiding contact with infected animals and taking precautions to prevent flea bites. In some cases, prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended.


