N-Methylserotonin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Norbufotenine.svg|Norbufotenine chemical structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 05:36, 3 March 2025
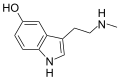
N-Methylserotonin is a naturally occurring compound found in the human body. It is a derivative of the neurotransmitter serotonin, which plays a crucial role in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep. N-Methylserotonin is believed to have similar effects on the body, although research into its specific functions and potential therapeutic uses is ongoing.
Chemical Structure and Synthesis
N-Methylserotonin is a tryptamine derivative, meaning it is structurally related to the amino acid tryptophan. It is synthesized in the body through the methylation of serotonin, a process catalyzed by the enzyme serotonin N-methyltransferase. This enzyme adds a methyl group to the nitrogen atom of serotonin, resulting in the formation of N-Methylserotonin.
Physiological Effects
Like serotonin, N-Methylserotonin is believed to act as a neurotransmitter, facilitating communication between nerve cells in the brain. It may also have a role in regulating mood and sleep, although the exact mechanisms by which it exerts these effects are not fully understood.
Potential Therapeutic Uses
Research into the potential therapeutic uses of N-Methylserotonin is ongoing. Some studies suggest that it may have antidepressant and anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects, similar to those of serotonin. However, further research is needed to confirm these findings and to determine the safety and efficacy of N-Methylserotonin as a therapeutic agent.
See Also
-
Norbufotenine chemical structure