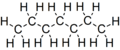Heptane: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
== Heptane == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Heptane-2D-Skeletal.svg|Heptane 2D Skeletal | |||
File:HeptaneFull.png|Heptane Full | |||
File:Heptane_3D_ball.png|Heptane 3D Ball | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 20:55, 23 February 2025
Heptane is a straight-chain alkane with the chemical formula C7H16. It is a colorless liquid that boils at 98.42 °C and has a slightly sweet smell similar to that of petroleum. Heptane is used in laboratories as a non-polar solvent. It is also used as a fuel in certain types of racing cars.
Chemical Properties
Heptane is a hydrocarbon of the alkane series. It is composed of seven carbon atoms linked together in a straight chain, with 16 hydrogen atoms attached. The chemical formula of heptane is C7H16. It is a non-polar molecule, which means it does not have a positive or negative charge and does not readily react with other substances.
Physical Properties
Heptane is a colorless liquid at room temperature. It has a slightly sweet smell, similar to that of petroleum. It boils at 98.42 °C and freezes at -90.6 °C. Heptane is less dense than water, with a density of 0.684 g/cm3 at 20 °C.
Uses
Heptane is used in laboratories as a non-polar solvent. It is also used as a fuel in certain types of racing cars. In addition, heptane is used in the production of rubber and plastics, and as a component in certain types of adhesives and paints.
Safety
Heptane is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. It can cause skin and eye irritation, and prolonged exposure can lead to central nervous system depression. It is also harmful if swallowed or inhaled.