Etoh: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{Alcohol-stub}} | {{Alcohol-stub}} | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
Latest revision as of 11:50, 17 March 2025
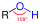
Ethanol (EtOH), also known as alcohol, is a chemical compound, a simple alcohol with the chemical formula C2H5OH. Its formula can also be written as CH3-CH2-OH or C2H5-OH (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group), and is often abbreviated as EtOH. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a slight characteristic odor. It is a psychoactive substance and is the principal type of alcohol found in alcoholic drinks.
Production[edit]
Ethanol is produced both by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts and by the petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. The fermentation process is the most common method for producing ethanol for consumption, while synthetic processes are used for the production of ethanol for industrial purposes.
Fermentation[edit]
In the fermentation process, Saccharomyces cerevisiae or other yeasts convert glucose, fructose, and sucrose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. The fermentation of one molecule of glucose produces two molecules of ethanol and two molecules of carbon dioxide, generating energy in the process.
Synthetic Production[edit]
Synthetic ethanol is produced by the hydration of ethylene, a process that involves the reaction of ethylene with water, in the presence of a catalyst, to produce ethanol. This method is commonly used to produce ethanol for use in industrial applications.
Uses[edit]
Ethanol is used in a wide variety of applications, from fuel and fuel additives to solvents, disinfectants, and beverages.
As a Fuel[edit]
Ethanol is used as a motor fuel by itself, as an ethanol-gasoline blend, or as an E85 fuel. It is considered a renewable fuel because it is primarily produced from biomass. Ethanol-blended fuel is widely used in Brazil and the United States.
In Beverages[edit]
Ethanol is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages such as beer, wine, and spirits. It is produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts.
Industrial Solvent and Disinfectant[edit]
Ethanol is used as a solvent in the manufacture of varnishes and perfumes; as a preservative for biological specimens; and as a disinfectant. It has a good solvency property for many organic compounds and is used in lotions, paints, and inks.
Health Effects[edit]
Ethanol acts as a central nervous system depressant and has significant psychoactive effects. Moderate consumption can have beneficial health effects for adults, such as reduced risk of heart disease. However, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to addiction, liver disease, and other chronic health problems.
Safety[edit]
Ethanol is flammable and should be handled with care. It should be stored in a cool, dry place away from sources of ignition.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Ethanol burns cleaner than gasoline, producing fewer greenhouse gases. However, the production of ethanol, especially from corn, can have significant environmental impacts, including the use of large amounts of water and land, and the potential for water pollution.