Tuberculin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Tuberculin == | == Tuberculin Skin Test == | ||
[[File:Mantoux_tuberculin_skin_test.jpg|thumb|A Mantoux tuberculin skin test | [[File:Mantoux_tuberculin_skin_test.jpg|thumb|right|A healthcare professional administering the Mantoux tuberculin skin test.]] | ||
''' | The '''tuberculin skin test''' (TST), also known as the '''Mantoux test''', is a diagnostic tool for [[tuberculosis]] (TB). It is used to determine if a person has been exposed to the [[Mycobacterium tuberculosis]] bacteria. The test involves the intradermal injection of a purified protein derivative (PPD) of the tuberculin antigen. | ||
== | == Procedure == | ||
The Mantoux test is performed by injecting a small amount of PPD tuberculin into the skin of the forearm. The injection is typically made on the inner surface of the forearm, about 4 inches below the elbow. The site is then observed for a reaction, which is measured in millimeters of induration (swelling) at the site of injection. | |||
== | === Reading the Test === | ||
The test site is examined 48 to 72 hours after the injection. A positive reaction is indicated by a raised, hardened area of induration. The size of the induration is measured and interpreted based on the individual's risk factors and history of exposure to TB. | |||
== | == Interpretation == | ||
The | The interpretation of the tuberculin skin test depends on the size of the induration and the individual's risk factors: | ||
* '''5 mm or more''' is considered positive in: | |||
* [[HIV]]-infected persons | |||
* Recent contacts of TB cases | |||
* Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with prior TB | |||
* Organ transplant recipients | |||
* Persons who are immunosuppressed for other reasons | |||
* '''10 mm or more''' is considered positive in: | |||
* Recent immigrants from high-prevalence countries | |||
* Injection drug users | |||
* Residents and employees of high-risk congregate settings | |||
* Mycobacteriology laboratory personnel | |||
* Persons with clinical conditions that place them at high risk | |||
* '''15 mm or more''' is considered positive in any person, including those with no known risk factors for TB. | |||
== Limitations == | == Limitations == | ||
The | The tuberculin skin test has several limitations. It cannot distinguish between latent TB infection and active TB disease. Additionally, false-positive results can occur in individuals who have been vaccinated with the [[Bacillus Calmette-Guérin]] (BCG) vaccine or exposed to non-tuberculous mycobacteria. False-negative results can occur in individuals with weakened immune systems. | ||
== | == Alternatives == | ||
An alternative to the tuberculin skin test is the [[interferon gamma release assay]] (IGRA), a blood test that measures the immune response to specific TB antigens. IGRAs are not affected by prior BCG vaccination and are often used in conjunction with the TST to improve diagnostic accuracy. | |||
== | == Related Pages == | ||
* | * [[Tuberculosis]] | ||
* | * [[Bacillus Calmette-Guérin]] | ||
* [[Interferon gamma release assay]] | |||
* [[Mycobacterium tuberculosis]] | |||
[[Category:Medical tests]] | |||
[[Category:Tuberculosis]] | [[Category:Tuberculosis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:25, 16 February 2025
Tuberculin Skin Test[edit]
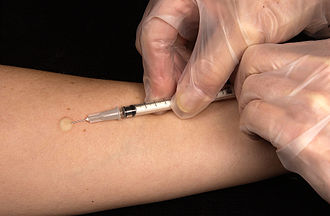
The tuberculin skin test (TST), also known as the Mantoux test, is a diagnostic tool for tuberculosis (TB). It is used to determine if a person has been exposed to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. The test involves the intradermal injection of a purified protein derivative (PPD) of the tuberculin antigen.
Procedure[edit]
The Mantoux test is performed by injecting a small amount of PPD tuberculin into the skin of the forearm. The injection is typically made on the inner surface of the forearm, about 4 inches below the elbow. The site is then observed for a reaction, which is measured in millimeters of induration (swelling) at the site of injection.
Reading the Test[edit]
The test site is examined 48 to 72 hours after the injection. A positive reaction is indicated by a raised, hardened area of induration. The size of the induration is measured and interpreted based on the individual's risk factors and history of exposure to TB.
Interpretation[edit]
The interpretation of the tuberculin skin test depends on the size of the induration and the individual's risk factors:
- 5 mm or more is considered positive in:
* HIV-infected persons * Recent contacts of TB cases * Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with prior TB * Organ transplant recipients * Persons who are immunosuppressed for other reasons
- 10 mm or more is considered positive in:
* Recent immigrants from high-prevalence countries * Injection drug users * Residents and employees of high-risk congregate settings * Mycobacteriology laboratory personnel * Persons with clinical conditions that place them at high risk
- 15 mm or more is considered positive in any person, including those with no known risk factors for TB.
Limitations[edit]
The tuberculin skin test has several limitations. It cannot distinguish between latent TB infection and active TB disease. Additionally, false-positive results can occur in individuals who have been vaccinated with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine or exposed to non-tuberculous mycobacteria. False-negative results can occur in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Alternatives[edit]
An alternative to the tuberculin skin test is the interferon gamma release assay (IGRA), a blood test that measures the immune response to specific TB antigens. IGRAs are not affected by prior BCG vaccination and are often used in conjunction with the TST to improve diagnostic accuracy.