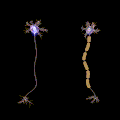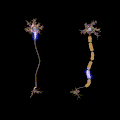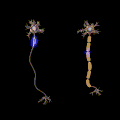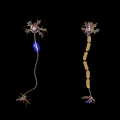Polyneuropathy: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
[[Category:Peripheral nervous system disorders]] | [[Category:Peripheral nervous system disorders]] | ||
{{nt}} | {{nt}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Vasculitic neuropathy - plastics - low mag.jpg|Polyneuropathy | |||
File:Saltatory Conduction.gif|Polyneuropathy | |||
File:Healthy Human T Cell.jpg|Polyneuropathy | |||
File:Ragged red fibres - gtc - very high mag.jpg|Polyneuropathy | |||
File:Methylprednisolone.png|Polyneuropathy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:26, 20 February 2025
Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy is a degenerative disease that affects the peripheral nerves, causing damage and dysfunction in various parts of the body. This condition can lead to a wide range of symptoms, depending on the nerves affected, and can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Overview
Polyneuropathy involves the damage or disease affecting multiple peripheral nerves. Unlike mononeuropathy, which affects a single nerve, polyneuropathy tends to have a more widespread impact on the body’s ability to sense and move.
Types
- Axonal neuropathy: Affects the nerve axons
- Demyelinating neuropathy: Involves the myelin sheath, the protective covering of the nerves
- Diabetic neuropathy: Caused by long-standing diabetes
- Guillain-Barré syndrome: An acute form that rapidly progresses
Causes
Polyneuropathy can result from several factors, including:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in Vitamin B12
- Chronic alcoholism
- Autoimmune diseases
- Genetic predispositions
- Toxic exposure to chemicals or medications
- Infections, such as HIV/AIDS and Lyme disease
Symptoms
Symptoms of polyneuropathy can vary but commonly include:
- Tingling and numbness in the hands or feet, spreading to the arms and legs
- Weakness in the muscles, especially in the feet and hands
- Loss of reflexes
- Pain, often described as burning, stabbing, or tingling
- Difficulty with coordination and balance
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and specific tests, including:
- Nerve conduction studies
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Blood tests to identify underlying causes
- Nerve biopsy in some cases
Treatment
While there's no cure for polyneuropathy, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and underlying causes:
- Medications for pain relief, such as gabapentin or pregabalin
- Physical therapy to improve muscle strength and coordination
- Treatment of underlying conditions, such as controlling blood sugar in diabetes
- Nutritional supplements for deficiencies
Management
Managing polyneuropathy involves:
- Regular monitoring and treatment adjustment
- Lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise
- Avoiding factors that can worsen the condition, such as alcohol
See Also
External Links
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke - Polyneuropathy
- The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy
References
<references/>
- "Polyneuropathy in Diabetes." Diabetes Care. [1]
- "Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy." Neurology. [2]
External links
|
|
|
-
Polyneuropathy
-
Polyneuropathy
-
Polyneuropathy
-
Polyneuropathy
-
Polyneuropathy