Tridentate ligand: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Tridentate Ligand == | |||
A '''tridentate ligand''' is a type of [[ligand]] that can form three bonds to a central [[metal]] atom or ion. These ligands are a subset of [[polydentate ligands]], which are capable of forming multiple bonds with a single metal center. Tridentate ligands are important in the field of [[coordination chemistry]] because they can stabilize metal complexes and influence their reactivity and properties. | |||
== | === Structure and Bonding === | ||
Tridentate ligands typically contain three donor atoms that can coordinate to a metal center. These donor atoms are often [[nitrogen]], [[oxygen]], or [[sulfur]] atoms, which have lone pairs of electrons that can be donated to the metal. The arrangement of these donor atoms allows the ligand to "wrap around" the metal, forming a stable complex. | |||
Tridentate ligands | |||
[[File:Mida.svg|thumb|right|MIDA ligand]] | |||
[[File:9-Crown-3.svg|thumb|right|9-Crown-3 ligand]] | |||
== | === Examples of Tridentate Ligands === | ||
== | Some common examples of tridentate ligands include: | ||
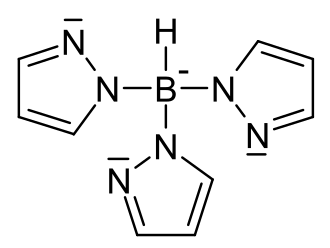
* '''Tris(pyrazolyl)borate''' - A ligand that contains three pyrazolyl groups attached to a central boron atom. It is often used in the synthesis of metal complexes. | |||
[[File:Tris(pyrazol)borat.svg|thumb|right|Tris(pyrazolyl)borate ligand]] | |||
* '''ToM ligand''' - A ligand with three donor atoms that can coordinate to a metal center. | |||
[[File:ToM_ligand.jpg|thumb|right|ToM ligand]] | |||
* '''ToP ligand''' - Similar to the ToM ligand, it has three donor atoms for metal coordination. | |||
[[File:ToP_ligand.jpg|thumb|right|ToP ligand]] | |||
* '''PMDTA''' (N,N,N',N'',N''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine) - A tridentate ligand with three nitrogen donor atoms. | |||
[[File:PMDTA.png|thumb|right|PMDTA ligand]] | |||
* '''Linear Triphos''' - A ligand with three phosphorus donor atoms arranged linearly. | |||
[[File:LinearTriphos.png|thumb|right|Linear Triphos ligand]] | |||
* '''1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane''' - A sulfur-containing tridentate ligand. | |||
[[File:1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane.svg|thumb|right|1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane ligand]] | |||
* '''Me3TACN''' (1,4,7-trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane) - A nitrogen-based tridentate ligand. | |||
[[File:Me3TACN.png|thumb|right|Me3TACN ligand]] | |||
* '''1,4,7-Triazacyclononane''' - A cyclic tridentate ligand with three nitrogen donor atoms. | |||
[[File:1,4,7-triazacyclononane.svg|thumb|right|1,4,7-Triazacyclononane ligand]] | |||
* '''Cis,cis-1,3,5-triaminocyclohexane''' - A ligand with three amine groups that can coordinate to a metal. | |||
[[File:Cis,cis-1,3,5-triaminocyclohexane.png|thumb|right|Cis,cis-1,3,5-triaminocyclohexane ligand]] | |||
=== Applications === | |||
Tridentate ligands are used in various applications, including: | |||
* '''Catalysis''': They are often used in [[catalysis]] to stabilize reactive metal centers and enhance catalytic activity. | |||
* '''Medicinal Chemistry''': Tridentate ligands can be used to design metal-based drugs with specific properties. | |||
* '''Material Science''': They are used in the synthesis of new materials with unique electronic or magnetic properties. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Ligand]] | |||
* [[Coordination chemistry]] | |||
* [[Chelation]] | * [[Chelation]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Polydentate ligand]] | ||
{{Coordination chemistry}} | |||
[[Category:Coordination chemistry]] | [[Category:Coordination chemistry]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Ligands]] | ||
Revision as of 00:41, 10 February 2025
Tridentate Ligand
A tridentate ligand is a type of ligand that can form three bonds to a central metal atom or ion. These ligands are a subset of polydentate ligands, which are capable of forming multiple bonds with a single metal center. Tridentate ligands are important in the field of coordination chemistry because they can stabilize metal complexes and influence their reactivity and properties.
Structure and Bonding
Tridentate ligands typically contain three donor atoms that can coordinate to a metal center. These donor atoms are often nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur atoms, which have lone pairs of electrons that can be donated to the metal. The arrangement of these donor atoms allows the ligand to "wrap around" the metal, forming a stable complex.


Examples of Tridentate Ligands
Some common examples of tridentate ligands include:
- Tris(pyrazolyl)borate - A ligand that contains three pyrazolyl groups attached to a central boron atom. It is often used in the synthesis of metal complexes.
- ToM ligand - A ligand with three donor atoms that can coordinate to a metal center.

- ToP ligand - Similar to the ToM ligand, it has three donor atoms for metal coordination.

- PMDTA (N,N,N',N,N-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine) - A tridentate ligand with three nitrogen donor atoms.

- Linear Triphos - A ligand with three phosphorus donor atoms arranged linearly.

- 1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane - A sulfur-containing tridentate ligand.

- Me3TACN (1,4,7-trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane) - A nitrogen-based tridentate ligand.

- 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane - A cyclic tridentate ligand with three nitrogen donor atoms.

- Cis,cis-1,3,5-triaminocyclohexane - A ligand with three amine groups that can coordinate to a metal.

Applications
Tridentate ligands are used in various applications, including:
- Catalysis: They are often used in catalysis to stabilize reactive metal centers and enhance catalytic activity.
- Medicinal Chemistry: Tridentate ligands can be used to design metal-based drugs with specific properties.
- Material Science: They are used in the synthesis of new materials with unique electronic or magnetic properties.
Related Pages
| Coordination Chemistry | |
|---|---|
|
Main concepts |
|
|
Types of ligands |
|
|
Applications |
|
|
Notable complexes |
|
|
Related topics |
|