Phosphite ester: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
== Phosphite_ester == | |||
<gallery> | |||
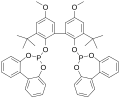
File:BigPhosphite31570-04-4.png|Structure of a large phosphite ester | |||
File:Triethylphosphitereduction.png|Reduction process involving triethyl phosphite | |||
File:BiPhePhos.svg|Structure of BiPhePhos ligand | |||
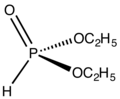
File:(EtO)2POH.png|Structure of diethyl phosphite | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:34, 18 February 2025
Phosphite esters are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a phosphorus atom bonded to three alkoxy groups. They are derived from phosphorous acid (H3PO3) and are important in various chemical reactions, particularly in the field of organic synthesis and as intermediates in the production of pesticides, flame retardants, and plasticizers.
Structure and Properties[edit]
Phosphite esters have the general formula P(OR)3, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group. The phosphorus atom in phosphite esters has a formal oxidation state of +3 and is bonded to three oxygen atoms, each of which is connected to a carbon-containing group. This structure imparts unique chemical properties to phosphite esters, including their reactivity and stability.
Synthesis[edit]
Phosphite esters are typically synthesized through the reaction of phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) with alcohols (ROH) in the presence of a base. This process, known as the Arbuzov reaction, is one of the most common methods for preparing phosphite esters. The reaction proceeds via the formation of an intermediate phosphorus compound, which then reacts with an alcohol to yield the desired phosphite ester.
Applications[edit]
Phosphite esters play a crucial role in various chemical processes and applications:
- Organic Synthesis: They are used as reagents in the Michaelis-Arbuzov reaction, which is important for the synthesis of phosphonates, compounds that are valuable in medicinal chemistry and agriculture.
- Plasticizers: Certain phosphite esters serve as plasticizers, substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity.
- Flame Retardants: Some phosphite esters are used in the manufacture of flame retardants, which are added to materials to inhibit or resist the spread of fire.
- Pesticides: Phosphite esters are precursors in the synthesis of a variety of pesticides, helping to protect crops from pests and diseases.
Safety and Environmental Considerations[edit]
While phosphite esters are valuable in many industrial applications, their production and use must be carefully managed to minimize potential environmental and health impacts. Some phosphite esters can be toxic or hazardous, necessitating proper handling, storage, and disposal practices.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>
Phosphite_ester[edit]
-
Structure of a large phosphite ester
-
Reduction process involving triethyl phosphite
-
Structure of BiPhePhos ligand
-
Structure of diethyl phosphite