Gephyronic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
== Gephyronic_acid == | |||
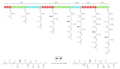
<gallery> | |||
File:Gephyronic_biosynthesis3.png|Gephyronic acid biosynthesis pathway | |||
File:Mechanism_of_SAM_O-methyltransferase.png|Mechanism of SAM O-methyltransferase | |||
File:Mechanism_of_p450_epoxidation.tif|Mechanism of P450 epoxidation | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:05, 18 February 2025
Gephyronic Acid is a natural product derived from the marine sponge species Geodia. It is a macrolide compound with a unique 18-membered macrocyclic lactone ring and two sugar moieties. Gephyronic acid has been found to exhibit potent antifungal activity, particularly against the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans.
Chemical Structure[edit]
The chemical structure of gephyronic acid is characterized by an 18-membered macrocyclic lactone ring, which is rare among natural products. The macrocycle is decorated with two sugar moieties, a deoxy sugar and a glycoside. The presence of these sugar moieties contributes to the compound's solubility and biological activity.
Biosynthesis[edit]
The biosynthesis of gephyronic acid is believed to involve a polyketide synthase (PKS) pathway. PKSs are large, multi-domain enzymes that catalyze the formation of complex polyketide structures from simple acyl-CoA precursors. The PKS pathway is thought to be responsible for the formation of the macrocyclic lactone ring and the attachment of the sugar moieties.
Biological Activity[edit]
Gephyronic acid has been found to exhibit potent antifungal activity, particularly against Candida albicans. This yeast species is a common cause of fungal infections in humans, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. The mechanism of action of gephyronic acid is believed to involve the inhibition of protein synthesis.
Clinical Potential[edit]
Due to its potent antifungal activity, gephyronic acid has potential for development as a novel antifungal drug. However, further studies are needed to fully understand its mechanism of action and to assess its safety and efficacy in humans.
See Also[edit]
Gephyronic_acid[edit]
-
Gephyronic acid biosynthesis pathway
-
Mechanism of SAM O-methyltransferase
-
Mechanism of P450 epoxidation