DOTA (chelator): Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
== DOTA (chelator) == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Tetraxetan_structure.svg|Tetraxetan structure | |||
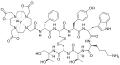
File:Y-90_tacatuzumab_tetraxetan_structure.svg|Y-90 tacatuzumab tetraxetan structure | |||
File:Yttrium-90_edotreotide.svg|Yttrium-90 edotreotide | |||
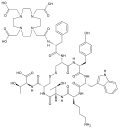
File:DOTATATE.svg|DOTATATE | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:48, 18 February 2025
DOTA (chelator)
1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (also known as DOTA) is an organic compound that is used as a complexing agent, specifically as a chelator in medicine. It is a white, crystalline powder that is soluble in water and has a slightly acidic pH.
Chemical Structure[edit]
DOTA is a macrocyclic compound, which means it has a large, ring-shaped structure. It consists of a 12-membered ring containing four nitrogen atoms and four carboxylic acid groups. The nitrogen atoms and the carboxylic acid groups are able to bind to metal ions, forming a stable complex.
Medical Uses[edit]
In medicine, DOTA is used as a chelating agent in the preparation of radiopharmaceuticals. It is able to form stable complexes with a variety of metal ions, including those used in medical imaging and therapy, such as gallium-68, lutetium-177, and yttrium-90. These complexes can be used in positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging, as well as in targeted radionuclide therapy.
Pharmacology[edit]
The pharmacology of DOTA is largely determined by the metal ion it is complexed with. The DOTA chelate acts as a carrier, delivering the metal ion to the desired location in the body. The properties of the metal ion, such as its radioactive decay and its interaction with biological tissues, determine the pharmacological effect.
Safety[edit]
DOTA is generally considered safe for use in humans. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and side effects. These can include allergic reactions, kidney damage, and radiation exposure. The risk of these side effects can be minimized by careful patient selection and monitoring.
See Also[edit]
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- Chelation Therapy
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
References[edit]
<references />
DOTA (chelator)[edit]
-
Tetraxetan structure
-
Y-90 tacatuzumab tetraxetan structure
-
Yttrium-90 edotreotide
-
DOTATATE