BOD (psychedelic): Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{Psychedelic-stub}} | {{Psychedelic-stub}} | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery caption="BOD (psychedelic)"> | |||
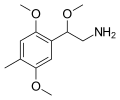
File:4-methyl-2,5,beta-trimethoxy-phenethylamine.svg|4-methyl-2,5,beta-trimethoxy-phenethylamine structure | |||
File:BOD-3d-sticks.png|BOD 3D stick model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 05:30, 3 March 2025
BOD (psychedelic)
BOD, also known as 4-methyl-2,5,beta-trimethoxyphenethylamine, is a psychedelic drug and substituted phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and documented in his book PiHKAL.
History
BOD was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 12–18 mg and the duration is listed as 8–16 hours. Shulgin classified BOD as a member of the so-called "magical half-dozen" which refers to Shulgin's self-rated most important phenethylamine-derived compounds.
Pharmacology
Like other 2C-x related molecules, BOD is believed to act as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist. However, the role of these interactions and how they result in the psychedelic experience continues to remain elusive.
Effects
The effects of BOD are not well documented, as it has seen very little human usage after its initial discovery. Anecdotal reports suggest that the effects are similar to other 2C-x related compounds and can include open and closed-eye visuals, time distortion, enhanced introspection, and ego loss.
Legal Status
As of 2021, BOD is not a controlled substance in any major jurisdiction, but its structural similarity to illegal 2C drugs could potentially subject possession, sale, or manufacture to legal prosecution under the Federal Analog Act in the United States.
See Also

This psychedelic-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
- BOD (psychedelic)
-
4-methyl-2,5,beta-trimethoxy-phenethylamine structure
-
BOD 3D stick model