Sparfloxacin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[Category:Fluoroquinolones]] | [[Category:Fluoroquinolones]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
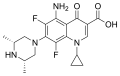
File:Sparfloxacin.svg|Chemical structure of Sparfloxacin | |||
File:Sparfloxacin-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png|3D model of Sparfloxacin from crystal structure | |||
File:Thermic_lance_principle.svg|Diagram illustrating the principle of a thermic lance | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:42, 18 February 2025
Sparfloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections. It is part of the third generation of fluoroquinolones, a class of synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotics, and is sold under the brand name Zagam.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Sparfloxacin works by inhibiting the DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes necessary for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. This inhibition prevents the bacteria from reproducing, thereby stopping the infection.
Medical Uses[edit]
Sparfloxacin is primarily used to treat respiratory tract infections, including community-acquired pneumonia and acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. It is also used in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections and urinary tract infections.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of Sparfloxacin include nausea, diarrhea, headache, and dizziness. Serious side effects may include tendon rupture, QT prolongation, and photosensitivity.
Contraindications[edit]
Sparfloxacin is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones, and in those with a history of epilepsy or other seizure disorders due to the risk of seizures.
Drug Interactions[edit]
Sparfloxacin may interact with other medications, including antacids, multivitamins, and didanosine, which can reduce its effectiveness. It may also interact with theophylline, increasing the risk of theophylline-related side effects.
See Also[edit]
- Fluoroquinolone
- Antibiotic
- DNA gyrase
- Topoisomerase IV
- Respiratory tract infection
- Community-acquired pneumonia
- Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis
- Skin and soft tissue infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Hypersensitivity
- Epilepsy
- Seizure
- Antacids
- Multivitamins
- Didanosine
- Theophylline
-
Chemical structure of Sparfloxacin
-
3D model of Sparfloxacin from crystal structure
-
Diagram illustrating the principle of a thermic lance