Operating system: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[Category:Software]] | [[Category:Software]] | ||
{{Computer-stub}} | {{Computer-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:IBM_system_360-50_console_-_MfK_Bern.jpg|IBM System/360 Model 50 Console | |||
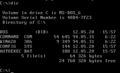
File:MS-Dos_screenshot.png|MS-DOS Screenshot | |||
File:System_1_File_Edit.png|System 1 File Edit | |||
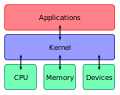
File:Kernel_Layout.svg|Kernel Layout | |||
File:Virtual_memory.svg|Virtual Memory | |||
File:Dolphin_FileManager.png|Dolphin File Manager | |||
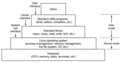
File:Layers_of_a_Linux_system.png|Layers of a Linux System | |||
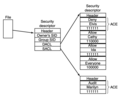
File:Diagram_of_a_security_descriptor_for_a_file_on_Windows.png|Security Descriptor for a File on Windows | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:25, 18 February 2025
Operating system (OS) is a type of software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides various services for computer programs. The operating system is an essential component of the system software in a computer system.
History[edit]
The concept of an operating system was first introduced in the 1950s with the development of the earliest mainframe computers. Early operating systems were very different from the sophisticated, multi-tasking systems we use today. They were simple programs designed to manage and control hardware resources, such as memory, I/O devices, and storage devices.
Functions[edit]
The primary functions of an operating system include managing the computer's resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, disk drives, and printers, providing an interface for users to interact with the system, and running applications.
Process Management[edit]
The operating system manages processes in a system. This includes the creation, scheduling, termination, and synchronization of processes.
Memory Management[edit]
The operating system is responsible for managing the computer's memory, including the RAM and the hard disk drive.
File System Management[edit]
The operating system manages files on the computer, including creating, deleting, moving, and copying files.
Device Management[edit]
The operating system manages the interaction between the user and the hardware devices of the computer.
Types of Operating Systems[edit]
There are several types of operating systems, including batch, time-sharing, multiprocessing, real-time, network, distributed, and mobile operating systems.
Examples of Operating Systems[edit]
Examples of popular operating systems include Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix. Mobile devices typically run operating systems like Android or iOS.
See Also[edit]
-
IBM System/360 Model 50 Console
-
MS-DOS Screenshot
-
System 1 File Edit
-
Kernel Layout
-
Virtual Memory
-
Dolphin File Manager
-
Layers of a Linux System
-
Security Descriptor for a File on Windows