Youth unemployment: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{{Economics-stub}} | {{Economics-stub}} | ||
{{Sociology-stub}} | {{Sociology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:1_-_Hamburg_1._Mai_2014_06.JPG|Youth unemployment protest in Hamburg | |||
File:Youth_Unemployment_rate_in_OECD.svg|Youth Unemployment rate in OECD | |||
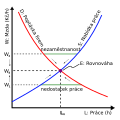
File:Labour-market-Supply-demand-Unemployment-cs.svg|Labour market supply and demand | |||
File:Aid_dependency.png|Aid dependency | |||
File:2011_Moroccan_protests_2.jpg|2011 Moroccan protests | |||
File:Job_Advertisement_Board_in_Shenzhen_-01.jpg|Job advertisement board in Shenzhen | |||
File:TVET_as_a_proportion_of_all_upper_secondary_programmes.svg|TVET as a proportion of all upper secondary programmes | |||
File:Media_Entrepreneurship_Definition.jpg|Media entrepreneurship definition | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:55, 18 February 2025
Youth Unemployment refers to the state of being without a job and actively seeking employment among individuals typically aged 15-24. This demographic is often the most affected by economic downturns and changes in the labor market.
Causes[edit]
Youth unemployment can be caused by a variety of factors, including economic recession, lack of job opportunities, lack of skills training and education, and discrimination.
Economic Recession[edit]
During an economic recession, businesses often cut back on hiring, which can disproportionately affect young people who are just entering the job market.
Lack of Job Opportunities[edit]
In some regions, there may be a lack of job opportunities suitable for young people. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as a decline in industries that traditionally employed young people, or a mismatch between the skills young people have and the skills employers are looking for.
Lack of Skills Training and Education[edit]
Without adequate skills training and education, young people may find it difficult to compete in the job market. This is particularly true in economies that are transitioning from manufacturing-based to knowledge-based.
Discrimination[edit]
In some cases, young people may face discrimination in the job market. This can be based on factors such as age, race, gender, or socioeconomic status.
Effects[edit]
Youth unemployment can have serious social and economic effects. These can include increased rates of poverty, crime, and mental health issues, as well as a loss of human capital for the economy as a whole.
Solutions[edit]
Solutions to youth unemployment can include policies aimed at increasing job creation, improving access to education and skills training, and combating discrimination in the job market.
See Also[edit]
- Unemployment
- Economic recession
- Job opportunities
- Skills training
- Education
- Discrimination
- Poverty
- Crime
- Mental health
-
Youth unemployment protest in Hamburg
-
Youth Unemployment rate in OECD
-
Labour market supply and demand
-
Aid dependency
-
2011 Moroccan protests
-
Job advertisement board in Shenzhen
-
TVET as a proportion of all upper secondary programmes
-
Media entrepreneurship definition