Unsupervised learning: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Type of machine learning algorithm}} | |||
{{Machine learning}} | |||
'''Unsupervised learning''' is a type of [[machine learning]] that involves training a model on data without explicit instructions on what to do with it. The model attempts to learn the underlying structure of the data by identifying patterns and relationships. Unlike [[supervised learning]], where the model is trained on labeled data, unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data. | |||
Unsupervised learning is | ==Overview== | ||
Unsupervised learning is used to draw inferences from datasets consisting of input data without labeled responses. The most common unsupervised learning tasks are [[clustering]] and [[association]]. | |||
* '''Clustering''': This involves grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (or cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. [[K-means clustering]] and [[hierarchical clustering]] are popular clustering algorithms. | |||
* '''Association''': This involves discovering interesting relations between variables in large databases. A common example is [[market basket analysis]], which is used to identify sets of products that frequently co-occur in transactions. | |||
== | ==Techniques== | ||
Several techniques are used in unsupervised learning, including: | |||
[[ | * '''[[Neural networks]]''': These are computational models inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected groups of artificial neurons. They are used in various unsupervised learning tasks. | ||
* '''[[Dimensionality reduction]]''': Techniques such as [[Principal Component Analysis]] (PCA) and [[t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding]] (t-SNE) are used to reduce the number of random variables under consideration. | |||
[[ | * '''[[Anomaly detection]]''': This involves identifying rare items, events, or observations that raise suspicions by differing significantly from the majority of the data. | ||
== Applications | ==Applications== | ||
Unsupervised learning is applied in various fields, including: | |||
* '''[[Image recognition]]''': Identifying patterns and features in images without prior labeling. | |||
* '''[[ | * '''[[Genomics]]''': Analyzing genetic data to find patterns and relationships. | ||
* '''[[Natural language processing]]''': Understanding and processing human language data. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Supervised learning]] | * [[Supervised learning]] | ||
* [[Reinforcement learning]] | * [[Reinforcement learning]] | ||
* [[Deep learning]] | * [[Deep learning]] | ||
== | ==Gallery== | ||
[[File:Task-guidance.png|thumb|Task guidance in unsupervised learning]] | |||
[[File:Hopfield-net-vector.svg|thumb|Hopfield network]] | |||
[[File:Boltzmannexamplev1.png|thumb|Boltzmann machine example]] | |||
[[File:Restricted_Boltzmann_machine.svg|thumb|Restricted Boltzmann machine]] | |||
[[File:Stacked-boltzmann.png|thumb|Stacked Boltzmann machine]] | |||
[[File:Helmholtz_Machine.png|thumb|Helmholtz machine]] | |||
[[File:Autoencoder_schema.png|thumb|Autoencoder schema]] | |||
[[File:VAE_blocks.png|thumb|Variational autoencoder blocks]] | |||
==References== | |||
* {{Cite book |last=Goodfellow |first=Ian |author-link=Ian Goodfellow |title=Deep Learning |year=2016 |publisher=MIT Press |isbn=978-0262035613}} | |||
* {{Cite journal |last=LeCun |first=Yann |author-link=Yann LeCun |title=Unsupervised Learning: Foundations of Neural Computation |journal=MIT Press |year=1998}} | |||
[[Category:Machine | [[Category:Machine learning]] | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 10 February 2025
Type of machine learning algorithm
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
|
|
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning that involves training a model on data without explicit instructions on what to do with it. The model attempts to learn the underlying structure of the data by identifying patterns and relationships. Unlike supervised learning, where the model is trained on labeled data, unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data.
Overview
Unsupervised learning is used to draw inferences from datasets consisting of input data without labeled responses. The most common unsupervised learning tasks are clustering and association.
- Clustering: This involves grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (or cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering are popular clustering algorithms.
- Association: This involves discovering interesting relations between variables in large databases. A common example is market basket analysis, which is used to identify sets of products that frequently co-occur in transactions.
Techniques
Several techniques are used in unsupervised learning, including:
- Neural networks: These are computational models inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected groups of artificial neurons. They are used in various unsupervised learning tasks.
- Dimensionality reduction: Techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) are used to reduce the number of random variables under consideration.
- Anomaly detection: This involves identifying rare items, events, or observations that raise suspicions by differing significantly from the majority of the data.
Applications
Unsupervised learning is applied in various fields, including:
- Image recognition: Identifying patterns and features in images without prior labeling.
- Genomics: Analyzing genetic data to find patterns and relationships.
- Natural language processing: Understanding and processing human language data.
Related pages
Gallery





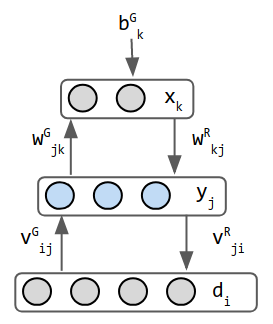


References
- Ian,
Deep Learning, MIT Press, 2016, ISBN 978-0262035613,
- LeCun, Yann,
Unsupervised Learning: Foundations of Neural Computation, MIT Press, 1998,