Industrial radiography: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{Industrial-process-stub}} | {{Industrial-process-stub}} | ||
{{Radiography-stub}} | {{Radiography-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:RT_Film_Making_a_Radiograph.jpg|Making a Radiograph | |||
File:GemX-200_(mb).png|GemX-200 | |||
File:VACIS_Gamma-ray_Image_with_stowaways.GIF|VACIS Gamma-ray Image with Stowaways | |||
File:Torchradiographycamerawithhinge.png|Torch Radiography Camera with Hinge | |||
File:Wheelradiographymachine.png|Wheel Radiography Machine | |||
File:Sshapedirradation_machine.png|S-shaped Irradiation Machine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:12, 18 February 2025
Industrial radiography is a method of non-destructive testing where many types of manufactured components can be examined to verify the internal structure and integrity of the specimen. Industrial Radiography can be performed utilizing either X-rays or gamma rays. Both are forms of electromagnetic radiation. The difference between various forms of electromagnetic radiation is the energy of the individual particles or photons.
History[edit]
Industrial radiography has grown out of engineering, and is a major element of nondestructive testing. It is a method of inspecting materials for hidden flaws by using the ability of short wavelength radiation (high energy photons) to penetrate various materials.
Safety[edit]
Safety is of paramount importance to the industrial radiographer. Some of the sources of radiation used in industrial radiography can cause serious injury or death in a short period of exposure. For this reason, industrial radiographers must be properly trained in radiation safety and certified by the relevant governmental or certifying bodies.
Applications[edit]
Industrial radiography is widely used in a variety of industries, including the petroleum industry, the aerospace industry, and the nuclear industry. It is used to inspect a variety of products and equipment, such as welds, castings, forgings, and fabrications, for internal defects or damage.
Techniques[edit]
There are two main techniques used in industrial radiography: direct radiography and computed radiography. Direct radiography involves the use of film or other detectors to capture the image, while computed radiography uses a digital detector system.
See also[edit]
This industrial process related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.

This article is a Radiography stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
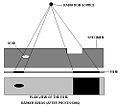
Making a Radiograph
-
GemX-200
-
VACIS Gamma-ray Image with Stowaways
-
Torch Radiography Camera with Hinge
-
Wheel Radiography Machine
-
S-shaped Irradiation Machine