ORF8: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
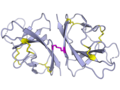
File:7jtl_sarscov2_orf8_dimer.png|SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Dimer Structure | |||
File:7jtl_orf8_7ci3_orf7a_superposition.png|Superposition of ORF8 and ORF7a Structures | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:44, 18 February 2025
ORF8 is a gene that is part of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The ORF8 gene is unique to the SARS-CoV-2 virus and is not found in other coronaviruses. It is believed to play a role in the virus's ability to evade the immune system and increase its virulence.
Function[edit]
The exact function of the ORF8 gene is not fully understood. However, it is believed to play a role in the virus's ability to evade the immune system. Studies have shown that the ORF8 protein can bind to the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) class I molecules and lead to their degradation, thereby preventing the immune system from recognizing and attacking the virus.
Structure[edit]
The ORF8 gene encodes a protein that is 121 amino acids in length. The protein has a unique structure that is not found in other coronaviruses. It is composed of two identical subunits that form a homodimer. The structure of the ORF8 protein allows it to bind to the MHC class I molecules and lead to their degradation.
Role in COVID-19[edit]
The ORF8 gene has been implicated in the severity of COVID-19. Studies have shown that mutations in the ORF8 gene can lead to a more severe form of the disease. In addition, the ORF8 gene is believed to play a role in the virus's ability to spread and cause disease.